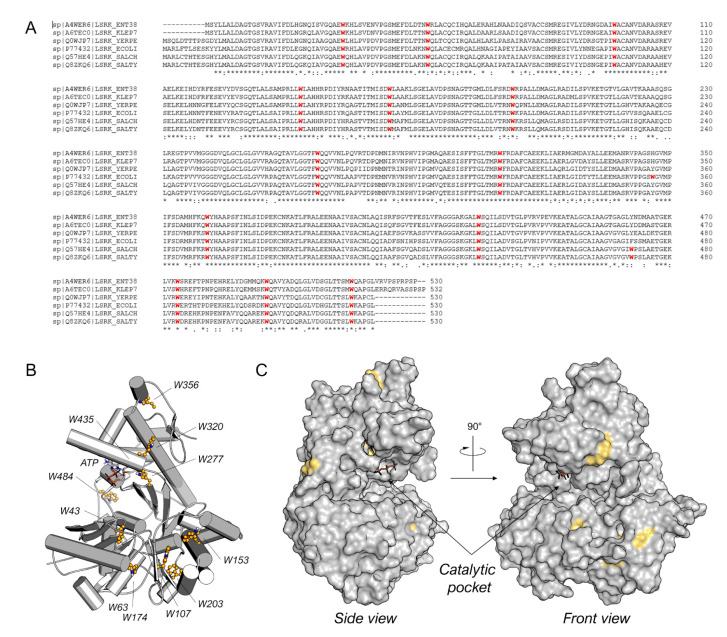
Figure 2.
(A) Sequence alignment for Enterobacter sp. (ENT38), K. pneumonia (KLEP7), Y. pestis (YERPE), E. coli (ECOLI), S. choleraesuis (SALCH), and S. typhimurium LsrK. All tryptophan residues are colored in red. Below the sequence alignment is a key denoting conserved amino acid residues (*), conservative substitutions (:), and semi-conservative substitutions (.). The non-conserved tryptophan residues between E. coli and S. typhimurium LsrK are highlighted in the red square. (B) Tryptophan residue position on the structure of ecLsrK (PDB ID: 5YA1). Lsrk is visualized as cartoons in grey. ATP is represented in stick mode. The tryptophan residues are highlighted in ball-and-stick with carbon atom in yellow. (C) Visualization of the tryptophan residues exposed on the surface of the protein. The putative catalytic pocket is indicated.