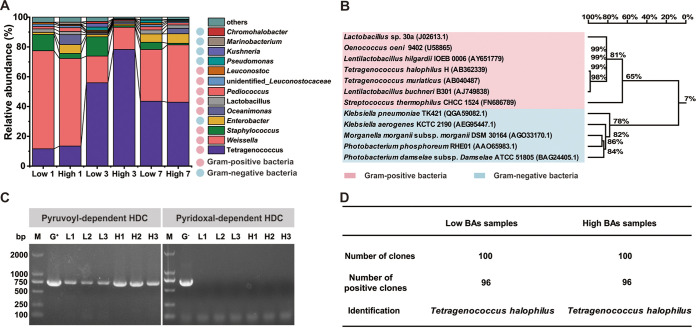
FIG 4.
Analysis of the focal histamine-producing microorganism during soy sauce fermentation. (A) Bacterial communities of soy sauce fermentation samples were collected at the 1st, 3rd, and 7th fermentation weeks. Low 1/3/7, bacterial community of low-histamine soy sauce samples which were collected at 1st, 3rd, and 7th fermentation weeks, respectively. High 1/3/7, bacterial community of high-histamine soy sauce samples which were collected at 1st, 3rd, and 7th fermentation weeks, respectively. (B) Analysis of histidine decarboxylase (HDC) protein sequence similarity between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. (C) Gene amplification of two kinds of histidine decarboxylase genes in low- and high-histamine soy sauce samples. M, marker; G+, gene amplification by using a Gram-positive bacterium genome as the template; G−, gene amplification by using the hdcA gene of Gram-negative bacteria added to fermented soy sauce moromi as the template; L1 to L3, three parallel soy sauce samples of low-histamine production; H1 to H3, three parallel soy sauce samples of high-histamine production. (D) Clone library analysis of hdcA gene in different soy sauce samples.