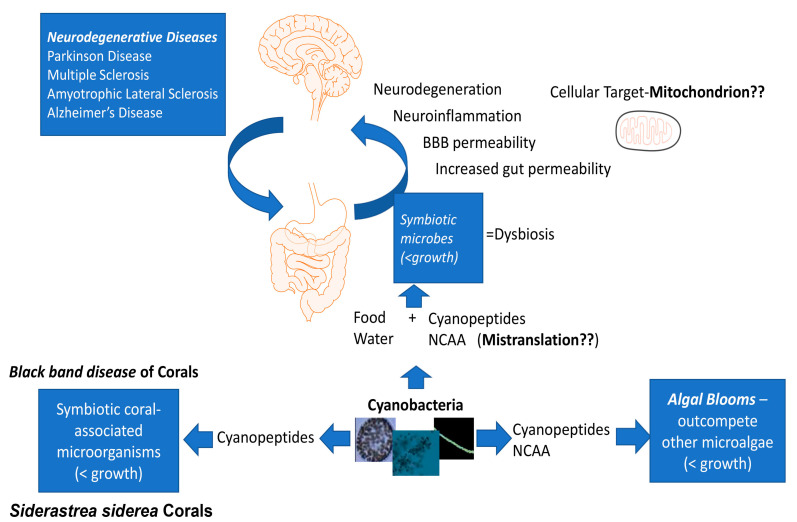
Figure 2.
“Cyanopeptides Hypothesis”. NCAA and cyanopeptides production by cyanobacteria that leads to mistranslation, proteostasis, and cellular growth delay may be an ancient mechanism developed initially to regulate the growth of other microorganisms and outcompete them. Outcompeting of symbiotic microorganisms may lead to disease development (examples: (1) Black Band disease of corals associated with cyclic peptides production by Roseophilum sp. cyanobacteria [350]; (2) association of the gut dysbiosis and ND such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases [351,352]). The mitochondria (likely evolved from prokaryotic endosymbionts) and cells that are high-energy demanding, such as neurons and cardiomyocytes, are likely to be affected by NCAA (example: BMAA induce mitochondrial dysfunction in neurons with cardiolipin exposure [353,354] and in embryonic cardiomyocytes leading to cardiac developmental defects [355].