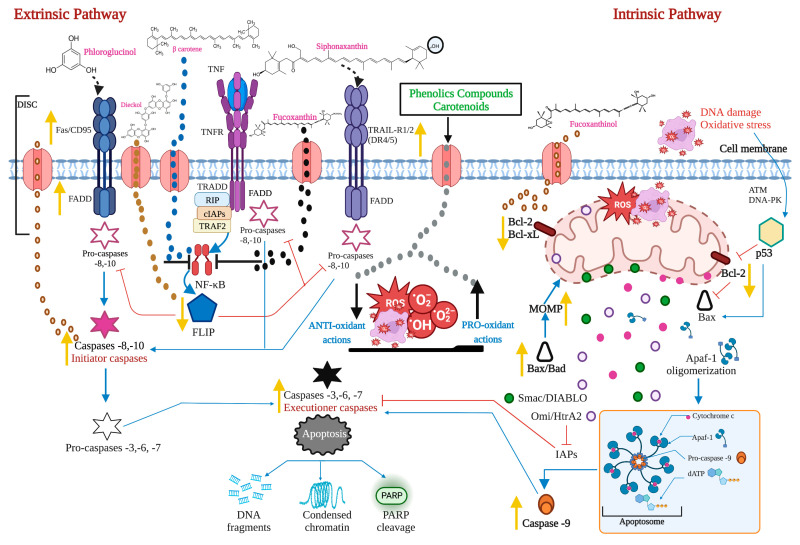
Figure 5.
Possible mechanism of action of phenolic compounds and carotenoids extracted from macroalgae inducing apoptosis. It represents the mechanism of action of some compounds such as phloroglucinol, dieckol, siphonaxanthin, fucoxanthin, and fucoxanthinol in the extrinsic and intrinsic pathway of apoptosis, modulating target molecules involved in them. Representation of the pro-oxidant action of phenolic compounds and carotenoids generates an overproduction of intracellular ROS, which causes mitochondrial dysfunction allowing the release of pro-apoptotic compounds to the cytosol, triggering apoptosis. Yellow arrows indicate positive or negative regulation of crucial proteins by these phenolic compounds and carotenoids. Apaf-1: apoptotic protease activating factor-1; ATM: Ataxia-telangiectasia-mutated; Bax: Bcl-2-associated X protein; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma; Bcl-xL: B-cell lymphoma-extra-large; Caspase -3, -6, -7, -8, -9, and 10: Cysteinyl aspartic acid-protease-3, -6, -7, -8, -9, and -10; DNA-PK: DNA-dependent protein kinase; DR 4/5: Death receptor 4/5; FADD: Fas-associated death domain; Fas: FLIP: (FADD-like IL-1β-converting enzyme)-inhibitory protein; HtrA2: High-temperature requirement protein A2; IAP: Inhibitors of Apoptosis Proteins; MOMP: Mitochondrial Outer Membrane Permeabilization; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; PARP: poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase; RIP: Receptor interacting protein; SMAC/DIABLO: Second mitochondrial activator of caspases/direct IAP binding protein with low PI; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TNFR1: TNF receptor 1; TRADD: TNF receptor-associated death domain; TRAF2: TNFR-associated factor 2; TRAIL: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand.