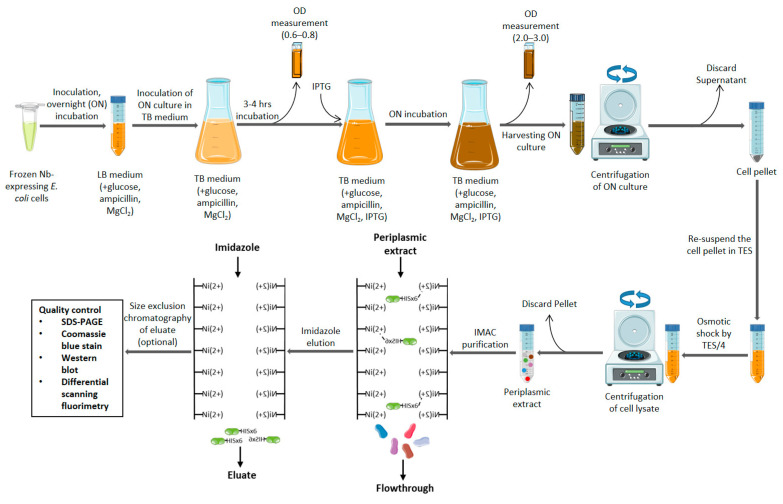
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of the conventional protocol for the laboratory scale production of Nbs starting from glycerol stock (frozen Nb expressing E. coli cells). LB medium (supplemented with glucose, ampicillin, and MgCl2) is inoculated with the glycerol stock and incubated overnight. This LB medium is used to inoculate a TB medium (supplemented with glucose, ampicillin, and MgCl2) and incubated for 3–4 h. Nb expression is induced via the addition of IPTG and incubated overnight. After each incubation, the absorbance is measured to ensure that cell multiplication (absorbance limit 0.6–0.8) and Nb expression (absorbance limit 2.0–3.0) occurred satisfactorily. The cell pellet of the TB medium is then aggregated through multiple rounds of centrifugation at 4000 RPM (using a tabletop centrifuge with TB medium in 50 mL falcon tubes) for 20 min each round. The aggregated cell pellet then undergoes periplasm lysis through the addition of a recommended quantity of TES buffer followed by the addition of TES/4 buffer. The periplasmic extract (supernatant) is then harvested through a round of centrifugation at 4000 RPM for 60 min using a tabletop centrifuge with TB medium in 50 mL falcon tubes) and the pellet is discarded. The periplasmic extract is then purified through IMAC and the Nb is eluted through the addition of imidazole. It is also possible to add a further purification step by size exclusion chromatography. The Nb then undergoes quality control via SDS-PAGE, Coomassie blue staining, western blotting, and differential scanning fluorimetry [71,78].