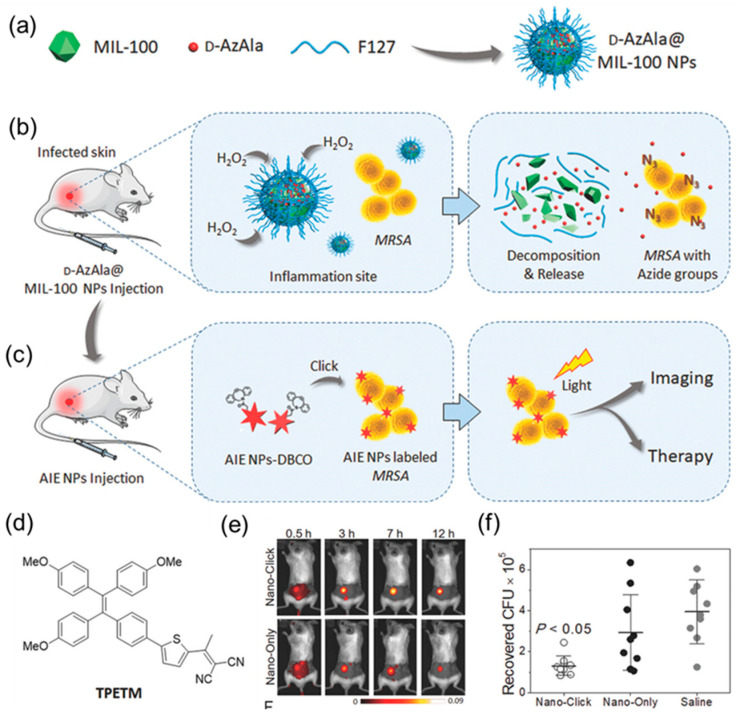
Figure 8.
(a) D-AzAla@MIL-100 (Fe) NPs are synthesized by using pluronic F-127 as a matrix to encapsulate the D-AzAla@MIL-100 (Fe). (b) D-AzAla@MIL-100 (Fe) NPs accumulate at the site of the infected tissue and are decomposed in the presence of H2O2. (c) Ultrasmall US-TPETM NPs with dibenzocyclooctyne (DBCO) groups bind with bacteria through click reactions, and specific tracking and effective photodynamic therapy (PDT) of bacteria can be achieved in the infected tissue. (d) Chemical structure of TPETM. (e) Time-dependent in vivo fluorescence images of bacteria-bearing mice pretreated with D-AzAla@MIL-100 (Fe) NPs. (f) Bacteria colony-forming unit (CFU) recovered from the infected skin (average ± the standard error of the mean (SEM). Adapted from [98], copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH.