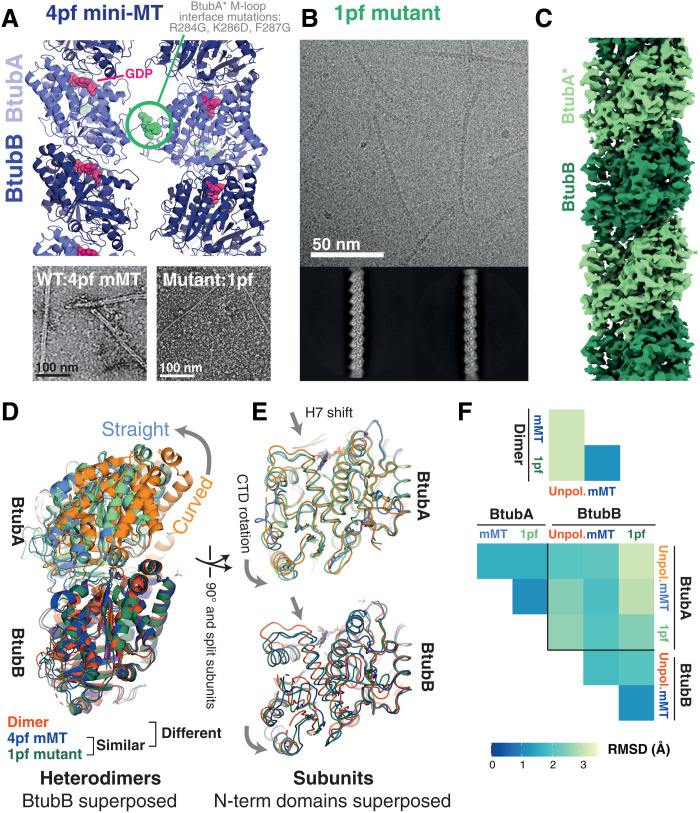
Fig. 4. Cryo-EM structures of a single protofilament tubulin reveals a polymerization-associated conformational switch.
(A) M-loop mutations in BtubA prevent lateral interactions between protofilaments (pf). Top: Side view of four-stranded mini-MT structure determined previously by cryo-EM (PDB 5O0C). M-loop residues 284 to 286 are shown as spheres in green. Bottom: Micrographs of negatively stained specimens: Left: 4pf mini-MT formed by WT BtubAB. Right: Single protofilament/1pf polymers formed by BtubA*B M-loop mutant (BtubA*: R284G, K286D, and F287G). (B) Cryo-EM study of BtubA*B polymerized using GMPCPP. Representative micrograph and 2D class averages are shown. Processing scheme can be found in fig. S7. Single filaments are also formed with GTP (see fig. S8). (C) Cryo-EM map of a single protofilament formed of BtubA*B polymerized using GMPCPP. (D and E) Comparison of BtubAB models from the dimeric (unpolymerized) crystal form (orange, PDB 2BTQ), the 4pf wt mini-MT (mMT, blue, PDB 5O09), and the single protofilament (1pf, M-loop mutant, PDB 7QUQ) solved here (green). Structures in (D) are aligned on the N-terminal domains of BtubB; structures in (E) are aligned on the N-terminal domains of the respective subunits. (F) Cα RMSD comparison of dimers (top) and individual subunit structures (bottom), following superposition as in (D) and (E). Polymerized heterodimers are highly similar.