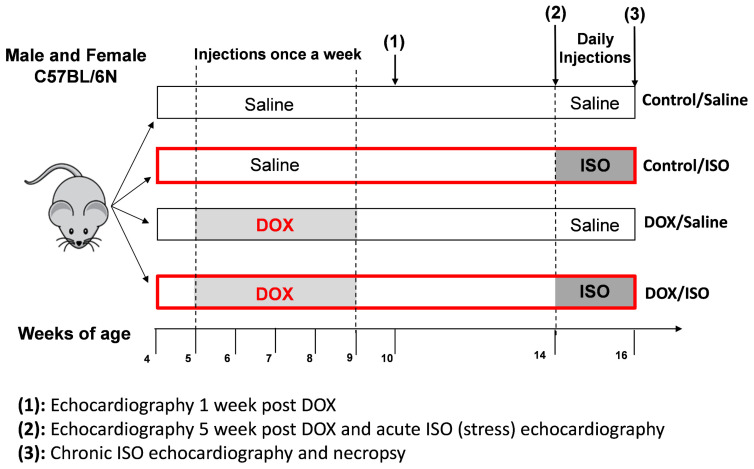
Figure 1.
Summary of the experimental design for DOX (4 mg/kg/week) and ISO (10 mg/kg/week) treatments. Male and female intact or gonadectomized mice were administered DOX or an equal volume of saline (control) at five weeks of age once a week for five consecutive weeks using intraperitoneal injections. After the last dose of DOX, mice were not administered treatment for the following five weeks. One (1) and five (2) weeks after the last DOX injection, baseline heart function was assessed with echocardiography. The ISO challenge began after the five-week recovery period. ISO or an equal volume of saline was administered subcutaneously for 14 consecutive days. Stress (acute ISO) echocardiography (2) was measured five minutes after the first ISO injection. Terminal echocardiography (3) was measured one day after the last ISO injection. After the final assessment of heart function, all mice were sacrificed, and tissues were collected for biochemical analysis. Abbreviations: DOX, doxorubicin; ISO, isoproterenol.