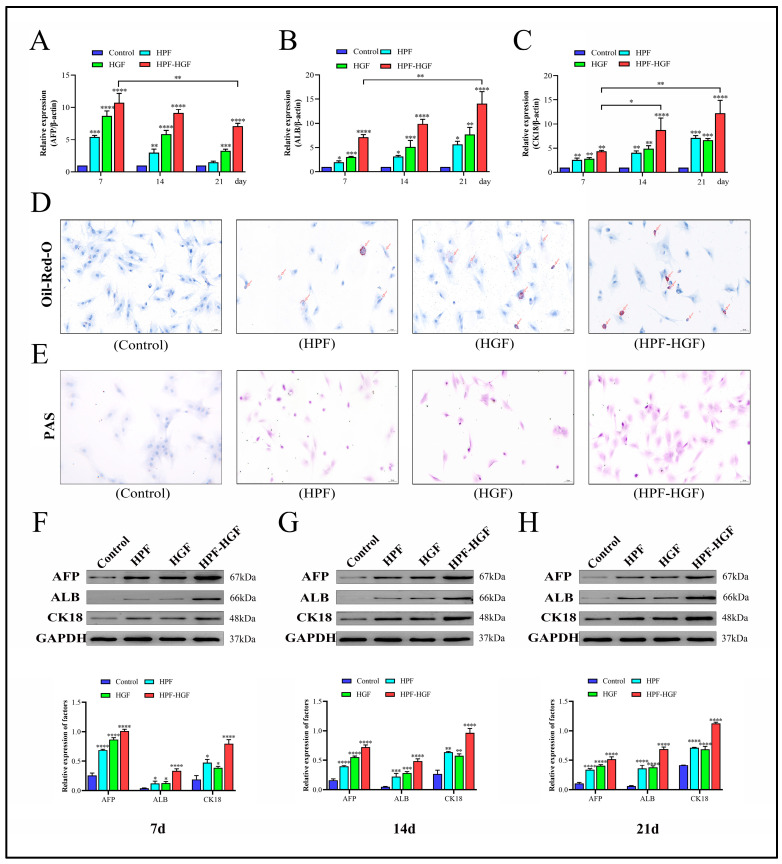
Figure 4.
Inducing BMSCs to differentiate into HLCs. (A) RT-qPCR was used to detect the expression of AFP in HPF-, HGF- and HPF–HGF-treated BMSCs and untreated BMSCs, at different time points. (B) RT-qPCR was used to detect the expression of ALB in HPF-, HGF- and HPF–HGF-treated BMSCs and untreated BMSCs at different time points. (C) RT-qPCR was used to detect the expression of CK18 in HPF-, HGF- and HPF–HGF-treated BMSCs and untreated BMSCs at different time points. (D) Representative images of BMSCs stained with Oil-Red-O show the ability of BMSCs to store lipids at 21 days of differentiation (200× magnification). (E) Representative images of BMSCs stained with PAS show the ability of BMSCs to store glycogen at 21 days of differentiation (200× magnification). (F) Expression of the hepatocyte markers AFP, ALB and CK18 in BMSCs treated with HPF, HGF and HPF–HGF for 7 days, as well as in untreated BMSCs, was detected by Western blot. (G) Expression of the hepatocyte markers AFP, ALB and CK18 in BMSCs treated with HPF, HGF and HPF–HGF for 14 days, as well as in untreated BMSCs, was detected by Western blot. (H) Expression of hepatocyte markers AFP, ALB and CK18 in BMSCs treated with HPF, HGF and HPF–HGF for 21 days, as well as untreated BMSCs, was detected by Western blot. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 and **** p < 0.0001 compared with the control group.