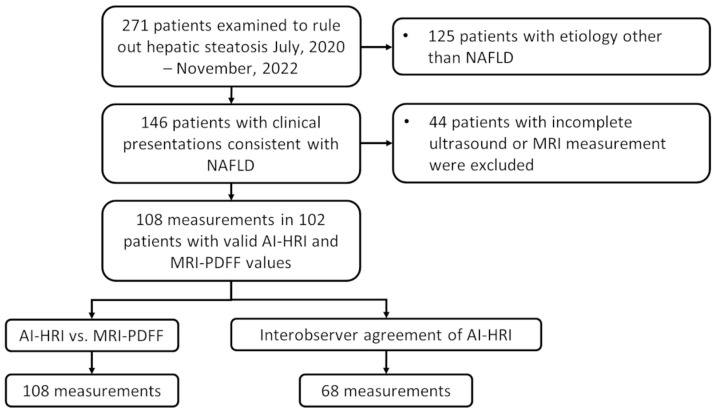
Figure 1.
The flowchart demonstrates patient selection and study design. We prospectively enrolled 102 participants with suspected non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in our study. Two hundred and seventy-one patients were referred to either an ultrasound or an MRI scan at our department to rule out hepatic steatosis; out of these, in 146 patients who did not show signs of acute liver failure, clinical findings were consistent with NAFLD. Forty-four patients who did not have a complete artificial intelligence-calculated hepatorenal index (AI-HRI) and magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF) measurements were excluded from the study. We evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of AI-HRI by comparing it to MRI-PDFF as a reference using 108 independent measurements of 102 patients. The interobserver agreement of AI-HRI was assessed in 68 cases, where measurements by two different examiners were available.