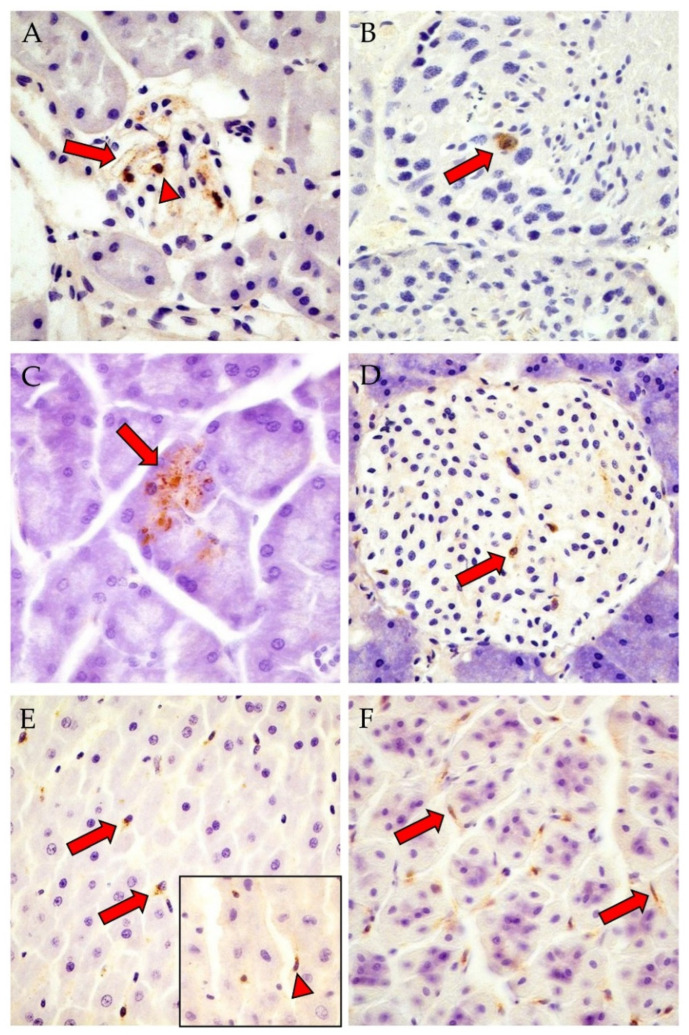
Figure 1.
Detection of PUUV nucleocapsid (N) protein in different tissues of OS (A,B,D,E, inset) and BF (C,F) bank voles by IHC. (A): male, RNA-positive, antibody-negative, kidney: positive endothelial cells (red arrow) and glomerulum cells (red arrowhead); (B): male, RNA-positive, antibody-positive, testis: sperm precursor cell with viral antigen (red arrow); (C): female, RNA-positive, antibody-positive, exocrine pancreas: positive acini (red arrow); (D): male, RNA-positive, antibody-positive, endocrine pancreas: positive islet cells of Langerhans (red arrow); (E): male, RNA-positive, antibody-negative, liver: positive Kupffer cells (red arrows); inset: female, RNA-positive, antibody-negative, N protein in cells with elongated spindle-shaped nuclei at sinusoid periphery (red arrowhead); (F): female, RNA-positive, antibody-positive, pars glandularis of the stomach: viral antigen in interstitial cells with lancet to spindle-shaped nuclei (red arrows). Total magnification: 400×. Corresponding positive signals in OS or BF voles are shown in Figure S5. IHC images of kidney, pancreas, liver and pars glandularis of the stomach of the negative control vole are shown in Figure S4.