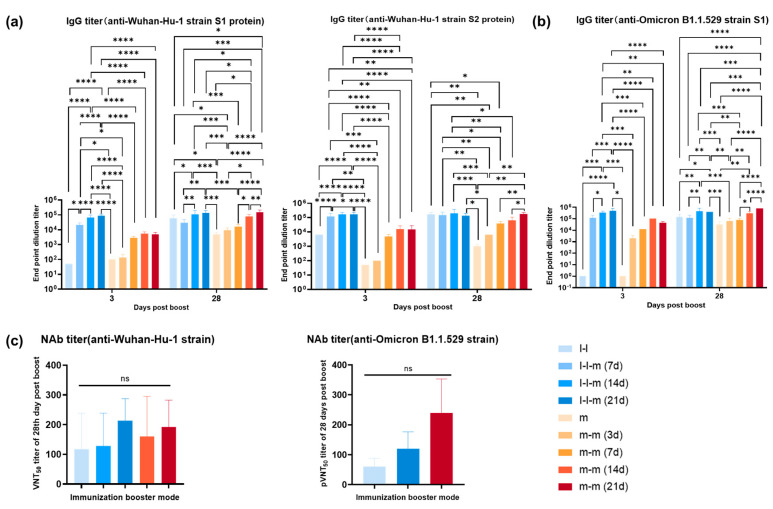
Figure 5.
Antibody responses elicited by two doses of an mRNA vaccine or two doses of an inactivated vaccine followed by an mRNA vaccine boost. (a) The specific IgG antibody levels against Wuhan-Hu-1 strain S1 and S2 were detected by ELISA at 3 days and 28 days post-boost immunization. Scheirer–Ray–Hare test was conducted. (b) The specific IgG antibody levels against Omicron strain (B.1.1.529) S1 were detected by ELISA at 3 days and 28 days post-boost immunization. Scheirer–Ray–Hare test was conducted. (c) Pseudovirus-neutralizing antibody assay against the Omicron strain (B.1.1.529) and virus-neutralizing antibody assay against the Wuhan-Hu-1 strain. One-way ANOVA (nonparametric or mixed) was conducted. Bars represent the mean ± SD. Group I-I (n = 15) was vaccinated with two doses of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (28-day interval), and groups I-I-m (7 d), I-I-m (14 d) and I-I-m (21 d) (n = 15 per group) were, respectively, vaccinated with the third dose of mRNA booster on days 7, 14 and 21 after the second dose. Group m (n = 10) was vaccinated with a dose of mRNA vaccine, and groups m-m (3 d), m-m (7 d), m-m (14 d) and m-m (21 d) (n = 10 per group) were vaccinated with the second dose of mRNA booster on days 3, 7, 14 and 21. Bars represent the mean ± SD. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001. ns, no significance.