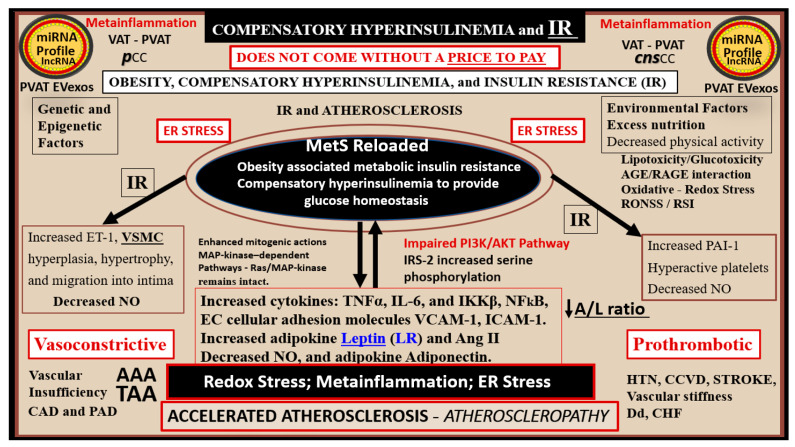
Figure 2.
Insulin resistance (IR) and compensatory hyperinsulinemia do not come without a price to pay. IR plays a central role in the MetS and results in an impaired PI3K/AKT pathway due to impaired IRS-2 function (IRS-2 increased serine phosphorylation) and decreased insulin-stimulated NO synthesis and impaired vasodilation. However, the elevated insulin can still signal through the mitogenic MAPkinase-dependent pathway and contribute to arterial vessel wall remodeling and accelerated atherosclerosis (atheroscleropathy) due to pro-atherosclerotic, pro-thrombotic, and vasoconstrictive effects). The increased redox stress and inflammatory vicious cycle that drive IR are promoted by an associated increased peripheral and central nervous cytokines and chemokines (pCC and cnsCC respectively) and the IR promoting effects from adipose-derived miRNAs via increased extracellular vesicle exosomes (EVexos) and their microRNA profiles along with the ongoing metainflammation. AAA = abdominal aortic aneurysm; Ang II = angiotensin II; CAD = coronary artery disease; CHF = congestive heart failure; ET-1 = endothelin-1; ER = endoplasmic reticulum; HTN = hypertension; ICAM-1= intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IKKβ = inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta; IL-6 = interleukin-6; lncRNA = long non-coding ribonucleic acid; LR = leptin resistance; miRNA = micro ribonucleic acid; NFkB = nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NO = nitric oxide; PAD = peripheral arterial disease; PAI-1 = plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; ROS = reactive oxygen species; RNA = ribonucleic acid; RONSS = reactive oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur species; RSI = reactive species interactome; TAA = thoracic aortic aneurysm; TNFα = tumor necrosis factor alpha; VCAM-1 = vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; VSMC = vascular smooth muscle cell(s).