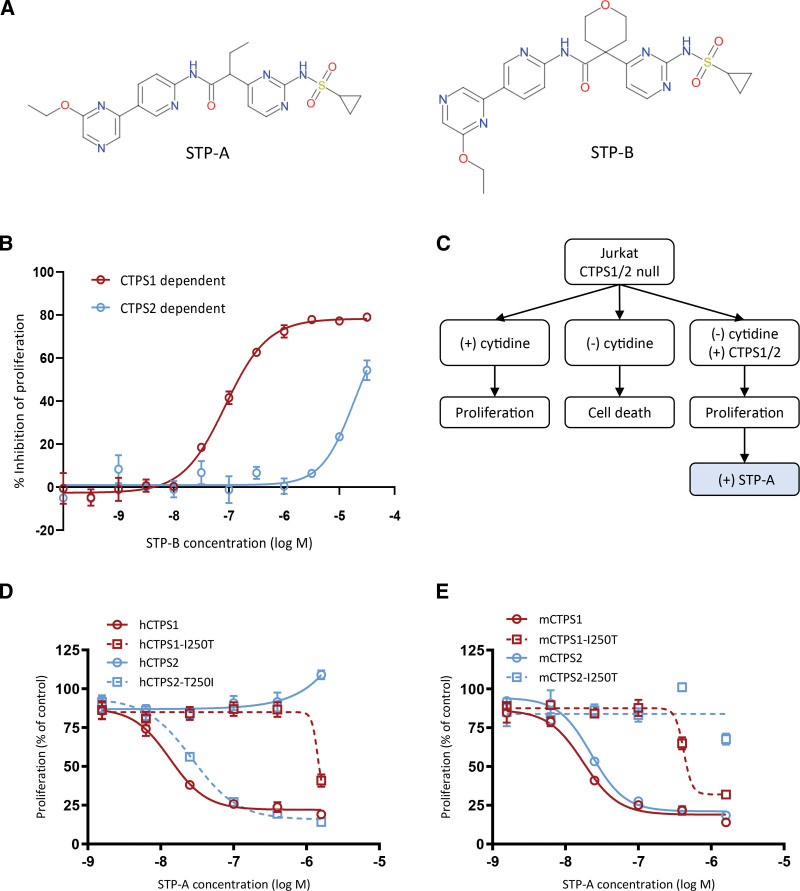
Figure 1.
Characterization of small molecule selective inhibitors of CTPS1. (A) Chemical structures of 2 selective CTPS1 inhibitors, STP-A and STP-B, derived from the same chemical series. (B) Proliferation of HEK cells deficient in CTPS2 or CTPS1 protein (and, therefore, dependent on CTPS1 or CTPS2, respectively, for proliferation) demonstrating the selectivity of STP-B for inhibition of CTPS1 over CTPS2. (C) Rationale and schema for CTPS1/2 complementation experiments. (D) Proliferation of cells complemented with native or mutant human CTPS1 or CTPS2 protein in the presence of increasing concentrations of STP-A, demonstrating the impact of residue 250 on the selectivity of the compound for CTPS1 over CTPS2. (E) Proliferation of cells complemented with native or mutant mouse CTPS1 or CTPS2 protein in the presence of increasing concentrations of STP-A, providing further support for the impact of residue 250 on the selectivity profile of these compounds. Graphs show means of triplicate values ± standard deviation. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments. CTPS = cytidine triphosphate synthase; HEK = human embryonic kidney.