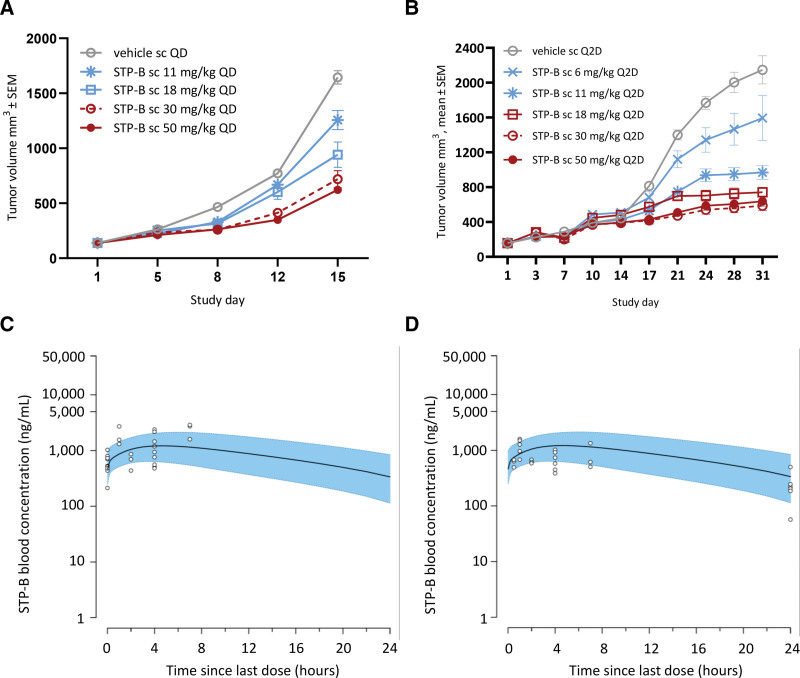
Figure 4.
Selective inhibition of CTPS1 inhibits the growth of human neoplastic lymphoid cells in vivo. (A) Tumor growth curves for neoplastic human B- cells (JEKO-1 mantle cell lymphoma) transplanted subcutaneously in SCID mice (n = 8 per group) showing dose-dependent inhibition of tumor growth by STP-B. (B) Tumor growth curves for neoplastic human T-cells (JURKAT T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia) transplanted subcutaneously in NOD-SCID mice (n = 8 per group) showing a dose-dependent inhibition of tumor growth by STP-B. (C/D) STP-B blood concentration vs time profiles at steady state predicted from a PK model (daily subcutaneous administration of STP-B at 30 mg/kg) overlaid with observed blood concentrations measured in satellite JEKO-1 (C) or JURKAT (D) tumor-bearing mice. Black line: median blood concentrations predicted by the PK model; blue shaded area: 90% prediction intervals; open circles: observed blood concentrations from sparse PK samples collected from tumor-bearing mice in a satellite cohort to the main efficacy study. CTPS = cytidine triphosphate synthase; PK = pharmacokinetics; NOD-SCID = nonobese diabetic, severe combined immunodeficiency disease; SEM = standard error of the mean.