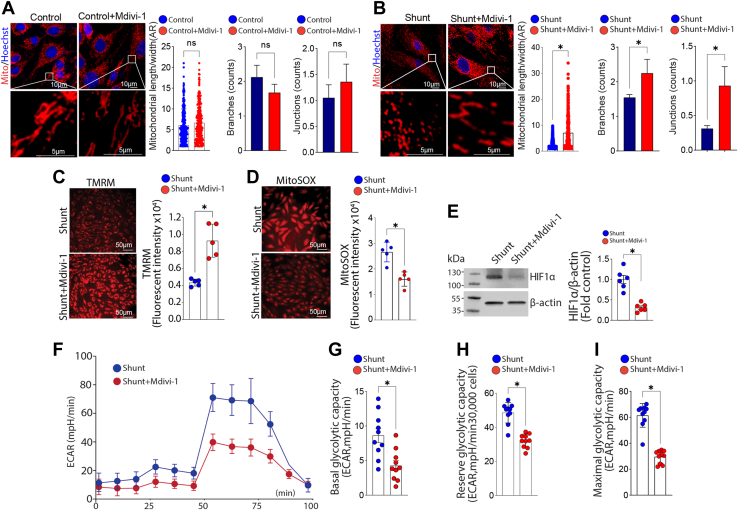
Figure 3.
Attenuating mitochondrial fission reduces mitochondrial dysfunction and cellular glycolysis in pulmonary arterial endothelial cells (PAECs) isolated from lambs with pulmonary hypertension. PAECs were treated or not with the Drp1 inhibitor, mdivi-1 (100 μM, 24 h), then the mitochondria were labeled with MitoTracker, and effects on mitochondrial fission were analyzed. Mdivi-1 exposure does not change the aspect ratio (AR), branches, and junctions counts in Control PAEC (A), but increases the AR and the number of mitochondrial branches and junctions in Shunt PAEC (B), indicative of increased mitochondrial fusion. Mdivi-1 also increases the mitochondrial membrane potential in Shunt PAEC (C) and decreases mt-ROS levels (D). Western blot analysis shows that HIF1α protein levels are decreased by mdivi-1 in Shunt PAEC (E). Representative images are shown. β-Actin was used to normalize protein loading. Mdivi-1 also decreases cellular glycolysis in Shunt PAEC (F), as evidenced by decreases in basal (G), reserve (H), and maximal (I) glycolytic capacity. The scale bar represents 10 μm. Data are mean ± SE. ∗p < 0.05 versus untreated Shunt PAEC.