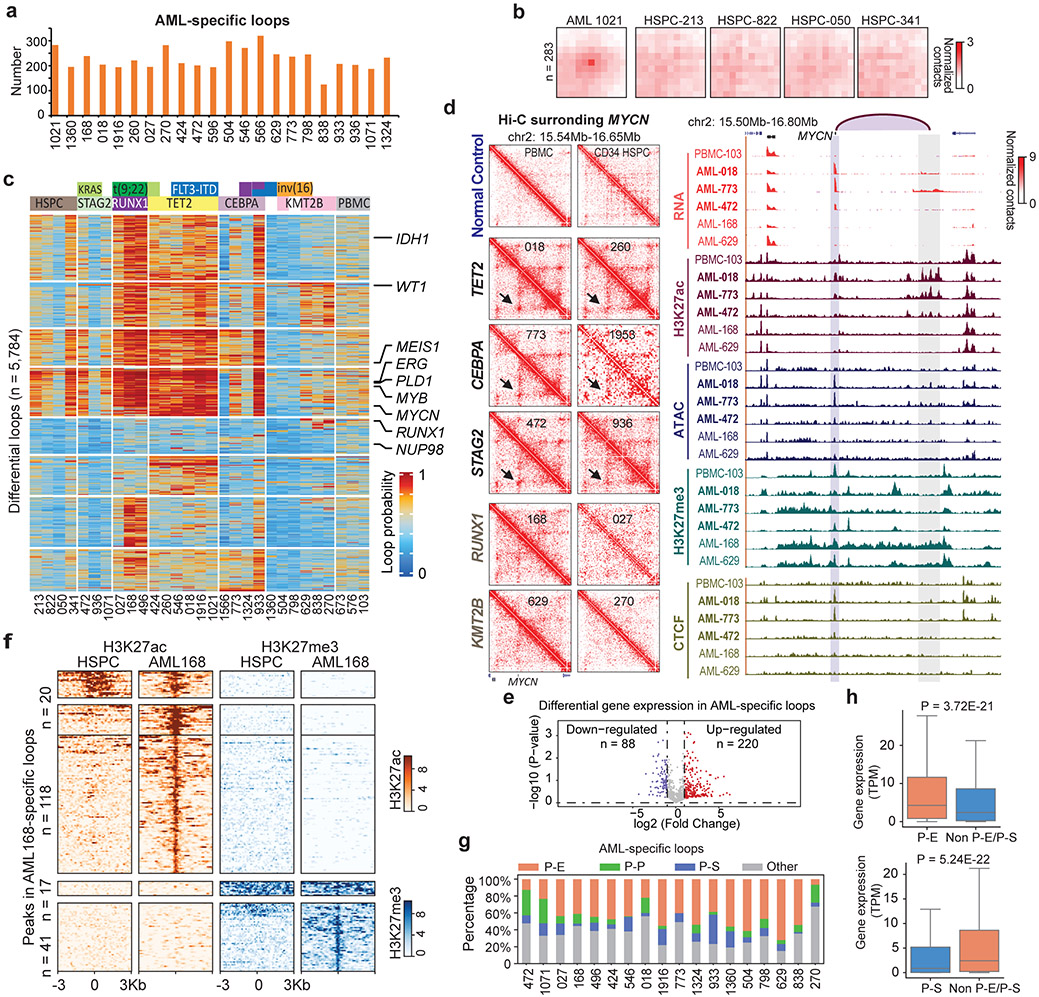
Figure 2 ∣. AML and subtype-specific chromatin loops.
a, Number of AML-specific loops by comparing with four CD34+ HSPC, using the Gaussian mixture model of Peakachu (FDR < 5%). 22 AML samples that have more than 100 million uniquely mapped reads and minimally 20 million long-range reads (>20Kb) were included for this analysis. b, APA plot for the AML 1021-specific loops vs. four HSPC controls. c, Subtype-specific loop analysis for AML samples. Each row is a loop and the values are the loop probabilities from Peakachu. d, From top to bottom, genome browser tracks for RNA-seq, ATAC-seq, and CUT&Tag for H3K27ac, H3K27me3, and CTCF. The purple arc marks the loop anchors, which link the MYCN promoter to distal enhancers in samples with TET2 and CEBA mutations. e, Differential expression analysis for genes in recurrent AML-specific loops vs. HSPC. P value by two-tailed t-test. f, Heatmap of H3K27ac and H3K27me3 peaks in the anchors of AML-specific loops (AML 168 vs. HSPC). g, P-E, promoter-enhancer loops; P-P, promoter-promoter loops; P-S, promoter-silencer loops. Enhancer and silencer annotations were based on H3K27ac and H3K27me3 signals. When enhancers and silencers are present in the same 10Kb loop anchor, the annotation was determined by the ratio of H3K27ac vs. H3K27me3 signals. Details in the method section. h, For each gene in a P-E or P-S loop anchor, AML samples were grouped into two categories: with the P-E/P-S loop, and without either P-E or P-S loop for this gene. Then the average gene expression (TPM) within each category was calculated. P value calculated by two-sided Kruskal-Wallis H-test. Upper: n=4,948 genes. Lower: n=1,508 genes. Box plot: middle line denotes median, top/bottom of boxes denotes first/third quartiles and whiskers extend to 1.5 times the interquartile range of the first and third quartile.