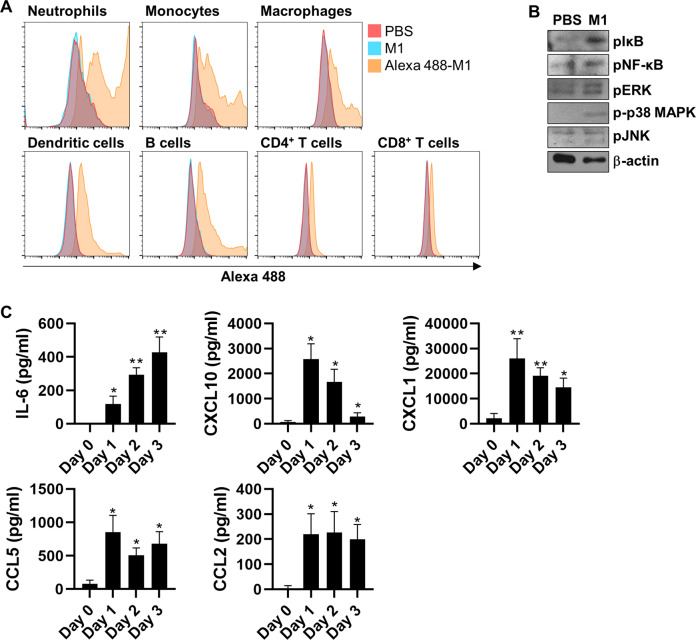
Fig. 4. M1 recognizes pulmonary immune cells and activates inflammatory responses in mouse lungs.
A Cells isolated from mouse lungs were treated with rM1 or Alexa 488-labeled rM1 (15 μg/ml) for 15 min and then analyzed by flow cytometry to determine the M1–cell association (n = 5). B Mice were intranasally treated with PBS or rM1 (15 μg/ml) for 6 h (n = 5). BAL fluid cells were isolated from these mice and subjected to immunoblotting to detect the activation of NF-κB and MAPK signaling. C Mice were intranasally treated with PBS or rM1 (30 μg/ml) for 0–3 days. BAL fluid was extracted from these mice and subjected to ELISA every day to measure the levels of the indicated cytokines and chemokines (n = 5). Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05.