Table 2.
Important N-glycosylation events in liver cancer.
| Protein | N-glycosylation events in liver cancer | Outcome/Application |
|---|---|---|
| E-Cadherin | Reduce bisecting N-glycan structure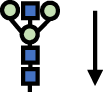
|
The interaction between E-Cadherin and β-catenin is weakened, and β-catenin enters the nucleus to activate the Wnt signaling pathway and promote the EMT process |
| CD44 | Increase sialylation levels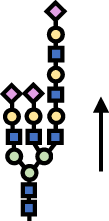
|
Promote the intercellular adhesion |
| Integrin | Raise sialylation and core fucosylation levels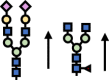
|
Inhibit the proliferation of liver cancer cells |
| Fibronectin | Elevate sialylation levels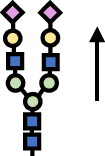
|
Influence its interaction with integrins, altering cell adhesion |
| Laminin | Increase the formation of β1, 6-branch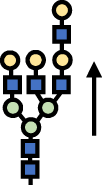
|
Enhance intercellular adhesion. |
| AFP | Expand core fucosylation levels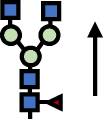
|
More reliable clinical diagnostic and prognostic indicator of liver cancer |
| AGP | Raise sialylation levels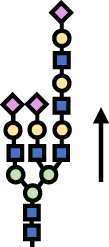
|
Increase diagnostic accuracy of liver cancer |
| Haptoglobin | Widen sialylation levels, lessen the formation of N-glycan branching structure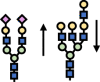
|
Reduce false negative results of diagnosis |
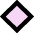 N-Acetylneuraminic acid
N-Acetylneuraminic acid  N-Acetylglucosamine
N-Acetylglucosamine 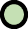 Mannose
Mannose 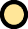 Galactose
Galactose
