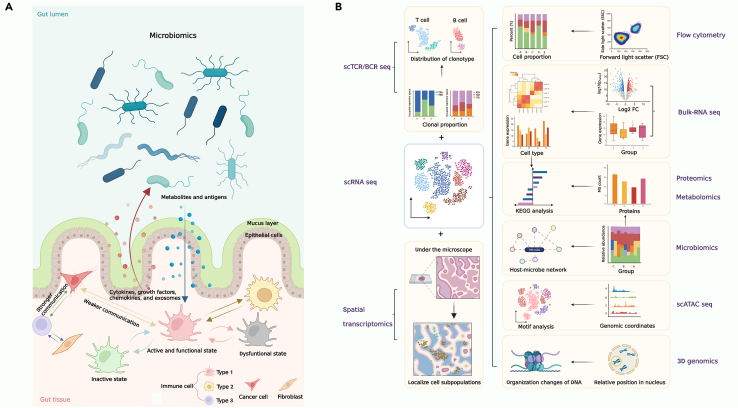
Figure 4.
The general illustration of how omics technologies are integrated to tackle complex biological problems in immunology
(A). Complex biological activities of immune cells: various immune cells have their own states including active and inactive, functional and dysfunctional. Different states can be explained by different trajectories of transcription and translation. Regulative processes and products in intracellular activities can be measured by single cell multi-omics tools and associated data can be acquired in each immune cell. Combination of each single cell multi-omics data can reveal the interactions and communications in the same type immune cells with different states, different types of immune cells, and other types of cells like cancer cells and cancer-related fibroblasts. Microbe-immune interplay can also be decoded by integration of microbiomics and multi-omics data. In addition, degree of communication may depend on the relative distance between cells.
(B) Integration of multi-omics approaches and associated data to understand the complexities of the human immune landscape.