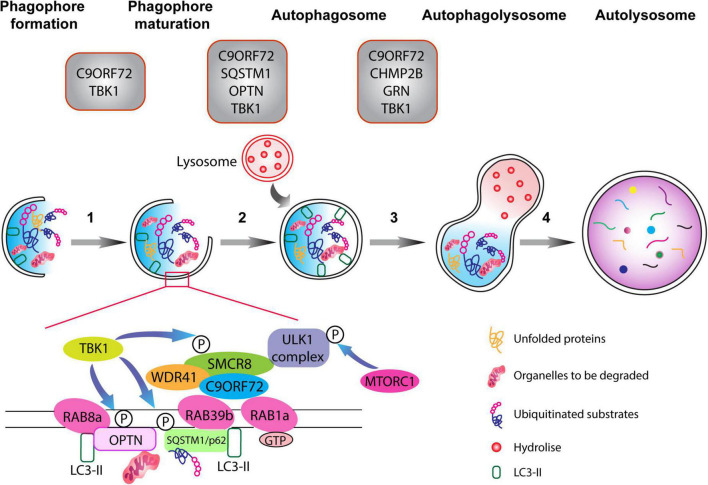
FIGURE 1.
The autophagy pathway. Schematic representation of different phases of the autophagy pathway from phagophore formation to the degradation of dysfunctional organelles and ubiquitinated proteins (the autophagic cargo) within autolysosomes. Top: gray boxes depict the various proteins associated with ALS-FTD that normally function at defined stages of the autophagolysosome formation. Autophagy is composed of multiple steps (1) phagophore formation, where double membrane phagophore forms around damaged molecules, unfolded proteins, and compromised organelles, (2) phagophore maturation and elongation, (3) the formation of the mature phagophore carrying the autophagic cargo, (4) the fusion of the phagosome with lysosome containing hydrolytic enzymes, which degrade the content of the autophagic cargo. The C9ORF72-WDR1-SMCR8 complex regulates autophagy at the initiation and progression phases (steps 1–3). RAB1a GTPase can recruit the C9ORF72 complex to engage the ULK1 complex during the initial phase of the autophagy pathway. Importantly, RAB8a and RAB39b, respectively, bind to OPTN and SQSTM1/p62, and also interact with the C9ORF72-WDR1-SMCR8 complex. Finally, phosphorylation of SCMR8 by TBK1 is crucial for the initiation of the autophagy pathway.