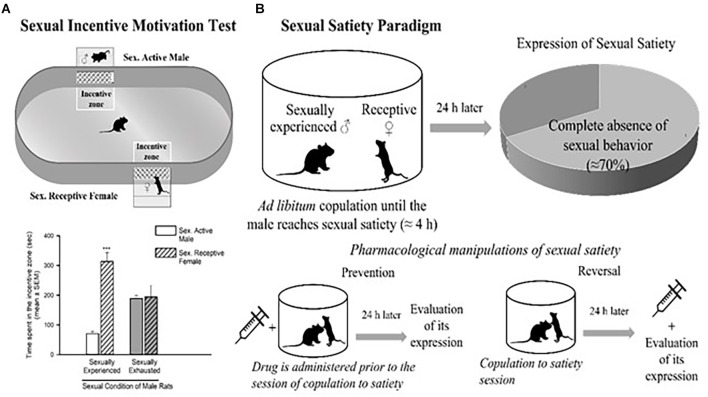
Figure 2.
Sexual incentive motivation test (A) and sexual satiety paradigm (B). Sexual incentive motivation is measured as the time spent by the male rat in the incentive zones (receptive female or male) of the test field. Sexually experienced males will spend more time in the incentive zone of the sexually receptive female (dashed bars) in comparison with the male (empty bars). Sexually satiated males will spend the same time in both incentive zones. In the sexual satiety paradigm, sexually experienced males in the course of an ad libitum copulation session will ejaculate repeatedly (7 in ≈4 h) until reaching sexual satiety. Twenty-four hours after copulation to satiety, most males (≈70%) will not respond with sexual behavior when a receptive female is accessible. Pharmacological treatments can modify the features of the sexual satiety paradigm, the most important being the increase in the percentage of sexually satiated male rats exhibiting sexual behavior expression with a receptive female. If a drug treatment is administered prior to the copulation to satiety session, the result (percentage of animals exhibiting sexual behavior) will reflect the prevention of the establishment of sexual inhibition. If the treatment is administered 24 h after the sexual satiety session, the result will reflect a reversal. Figures modified from Canseco-Alba and Rodríguez-Manzo (2019).