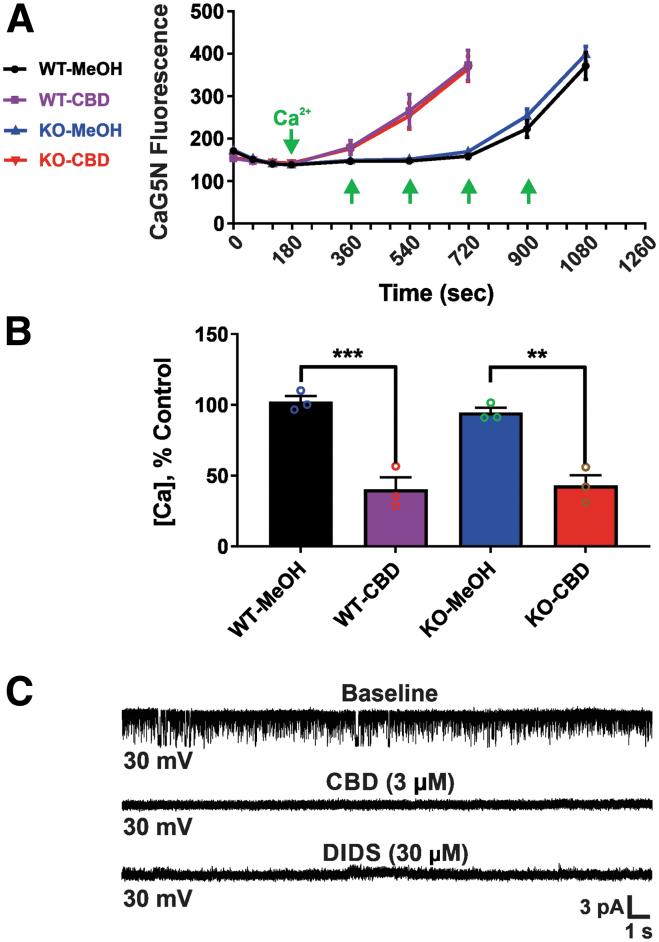
FIG. 4.
CBD effects are independent of CB1 receptors. CBD effects on mPT and mtCl channels are unaltered in acutely isolated mitochondria from CB1 KO mice compared with wild-type mice. (A) CBD at 3.75 μM significantly decreases the threshold for calcium-induced mPT in both wild-type and CB1 KO mice, as observed in normal Wistar rat brain. (Left) Ca2+ infusion traces. The y-axis of the graph is expressed in CaG5N fluorescence AU. (B) Bar graph depicting mean±SEM of mPT threshold (n=3 mice per group). The y-axis indicates the amount of Ca2+ added to the mitochondrial suspension. Data represent the mean±SEM, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test [F(3, 8)=(28.67), p=0.0001]. (C) Representative single-channel recording in CB1 KO mouse brain mitoplasts (n=3 per group) at a holding potential of +30 mV, showing that CBD (3 μM) and DIDS (30 μM) completely block chloride channel activity (indistinguishable from that seen in normal Wistar rat brain). CB1 KO, cannabinoid receptor type 1 knockout; DIDS, 4,4′-diisothiochanatostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid; mtCl, mitochondrial chloride.