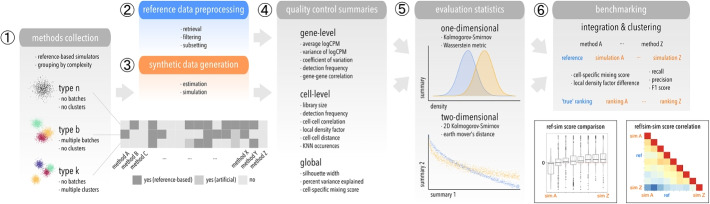
Fig. 1.
Schematic of the computational workflow used to benchmark scRNA-seq simulators. (1) Methods are grouped according to which level of complexity they can accommodate: type n (“singular”), b (batches), k (clusters). (2) Raw datasets are retrieved reproducibly from a public source, filtered, and subsetted into various datasets that serve as reference for (3) parameter estimation and simulation. (4) Various gene-, cell-level, and global summaries are computed from reference and simulated data, and (5) compared in a one- and two-dimensional setting using two statistics each. (6) Integration and clustering methods are applied to type b and k references and simulations, respectively, and relative performances compared between reference-simulation and simulation-simulation pairs