FIGURE 1.
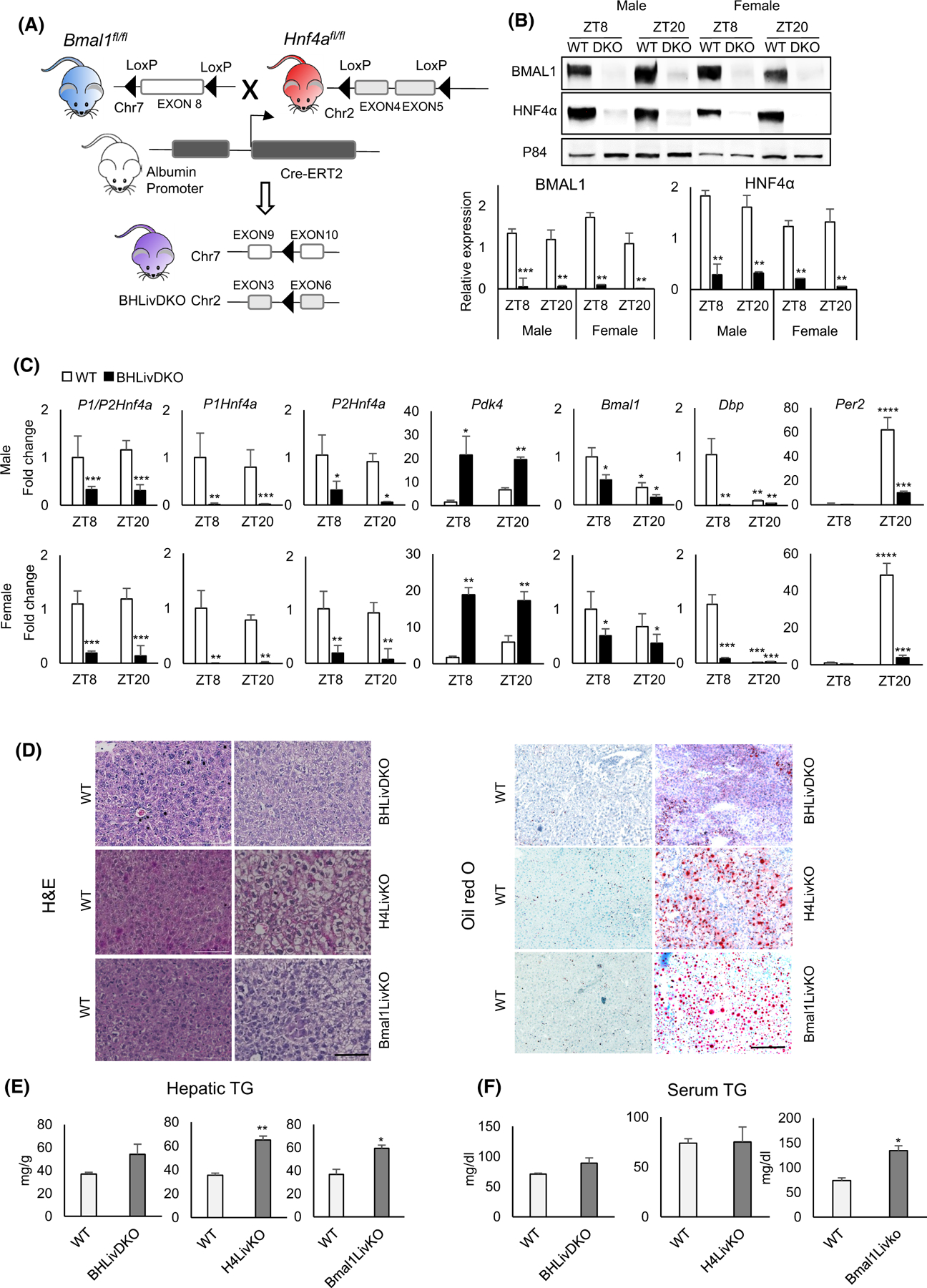
Loss of hepatic BMAL1 and HNF4α is protective against ectopic lipid deposition in the liver. (A) Mouse model of the hepatic Bmal1 and Hnf4a inducible double knockout (BHLivDKO). (B) Western blot of BMAL1 and HNF4α in the liver of BHLivDKO mice 10 days post-tamoxifen injection. Quantification of the immunoblots normalized to P84 (bottom panels). Student’s t-test. **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001. (C) Hepatic gene expression in WT and BHLivDKO measured by qPCR. Two-way ANOVA, Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (N = 6–8): *p < .03; **p < .005; ***p < .0005. (D) H&E (left panel) and Oil Red O (right panel) staining of WT, BHLivDKO, H4LivKO and Bmal1LivKO (Scale bar = 100 μm). (E and F) Hepatic (E) and serum (F) triglyceride levels in WT, BHLivDKO and H4LivKO mice. Significance (p < 0.05) was determined by Mann–Whitney U-test.
