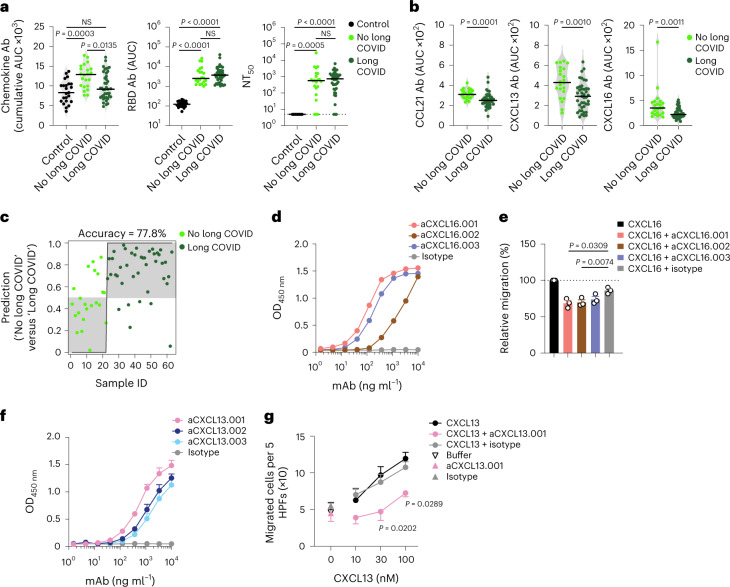
Fig. 2. Autoantibodies against specific chemokines in COVID-19 convalescents without persistent symptoms at month 12.
a, Chemokine IgG (cumulative AUC of ELISA; left), RBD IgG (middle) and NT50 (right) values in healthy controls (Controls) and COVID-19 convalescents (COVID-19) of the Lugano cohort at month 6 grouped as long COVID and no long COVID at month 12. Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test. b, AUC of ELISA showing CCL21, CXCL13 and CXCL16 antibodies (long COVID signature) at month 6 in COVID-19 convalescents defined as long COVID and no long COVID at month 12. Two-tailed Mann–Whitney U-tests. c, Logistic regression analysis showing the assignment of COVID-19 convalescents as long COVID and no long COVID at month 12, based on CCL21, CXCL13 and CXCL16 antibodies at month 6. d, ELISA showing CXCL16 antibodies binding to the CXCL16 N-loop peptide. Average of two independent experiments. e, Chemotaxis showing relative migration of the 300.19 preB cell line uniquely expressing CXCR6 in a CXCL16 gradient (1 nM). Mean + s.e.m. of three independent experiments. Paired, two-tailed Student’s t-test. f, ELISA showing CXCL13 antibodies binding to the CXCL13 N-loop peptide. Average of four independent experiments (mean + s.e.m.). g, Chemotaxis of primary CD19+ human B cells isolated from buffy coats in a CXCL13 gradient in the presence of the aCXCL13.001 antibody or isotype control. Mean ± s.e.m. of migrated cells in five high-power fields (HPFs). Average of three independent experiments with cells from different donors. Two-way repeated measures ANOVA followed by Šídák’s multiple comparisons test. In a and b, horizontal bars indicate median values and data are shown as average AUC from two independent experiments. Healthy controls (n = 23) in a; COVID-19 convalescents without (n = 22) or with (n = 41) long COVID at month 12 in a, b and c. OD, optical density.