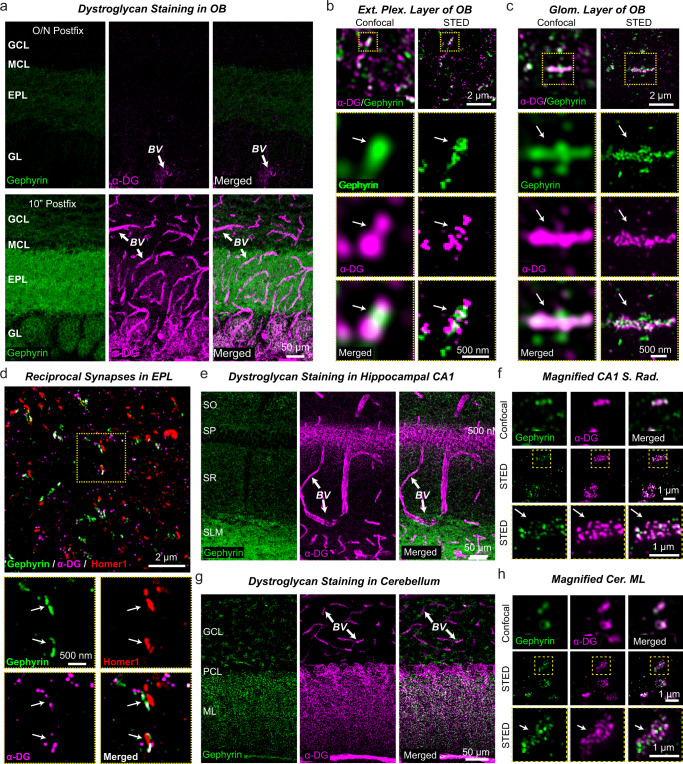
Fig. 7. α-Dystroglycan localizes to blood vessels and to inhibitory synapses in the OB.
a Only short post-fixation (10 min) but not overnight fixation (O/N) with 4% PFA allows efficient detection of gephyrin (green) and α-dystroglycan (purple) by immunocytochemistry in the OB (GCL, granule cell layer; MCL, mitral cell layer; EPL, external plexiform layer; GL, glomerular layer). Dystroglycan labeling in blood vessel (BV) walls is indicated with arrows. b Super-resolution imaging using stimulated emission depletion microscopy (STED) shows that inhibitory synapses in the EPL of the OB are often co-populated by dystroglycan nanoclusters. c STED super-resolution imaging reveals a similar nanocluster structure of gephyrin and dystroglycan at inhibitory synapses in the glomerular layer of the OB. d Specific labeling of reciprocal dendrodendritic synapses in OB sections demonstrates the presence of dystroglycan. Dendrodendritic synapses were identified by adjacent localizations of the inhibitory and excitatory postsynaptic markers gephyrin and Homer1, respectively. e, f Dystroglycan is abundantly present in perisomatic inhibitory synapses of pyramidal neurons in the hippocampal CA1 region in addition to BV walls. Sections were stained for gephyrin and α-dystroglycan (e, overview of a CA1 region section [SO, stratum oriens; SP, stratum pyramidale; SR, stratum radiatum; SLM, stratum lacunosome moleculare]; f, STED super-resolution imaging of the S. radiatum of the CA1 region demonstrating co-localization of dystroglycan with gephyrin). g, h Dystroglycan is also present at high levels in inhibitory synapses of the molecular layer of the cerebellar cortex. Sections were stained for gephyrin and α-dystroglycan (g, overview of the cerebellar cortex [GCL, granule cell layer; PCL, purkinje cell layer; ML, molecular layer]; h STED super-resolution imaging of the molecular layer of the cerebellar cortex again demonstrating co-localization of dystroglycan with the inhibitory synapse marker gephyrin). Experiments were performed at least three times and quantification of dystroglycan association with olfactory inhibitory synapses can be found in Fig. S8.