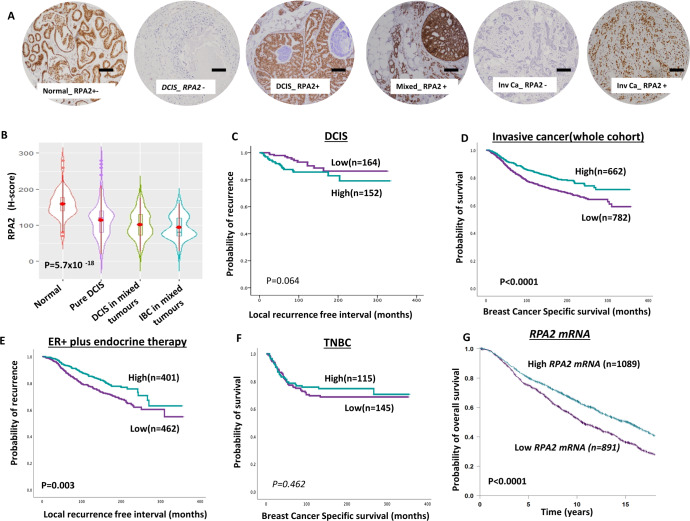
Fig. 2. Clinicopathological studies of RPA2 expression in breast cancers.
A Photomicrographs showing immunohistochemical staining of RPA2 in breast cancers (scale bar “−” = 100 µM). B Violin plot shows the mean of RPA2 expression in normal, pure DCIS and DCIS mixed tumours [The red dot represents the median, open red bar in the center represents the interquartile range, the thin red line represents the rest of the distribution, except for points that are “outliers”. On each side of the red line is a kernel density estimation to show the distribution shape of the data. Wider sections of the violin plot represent a higher probability that members of the population will take on the given value; the skinnier sections represent a lower probability.]. C Kaplan–Meier curve for RPA2 nuclear protein expression and recurrence-free interval (LRFI) in DCIS (D) a Kaplan–Meier curve for RPA2 nuclear protein expression and breast cancer-specific survival (BCSS) in the whole cohort. E Kaplan–Meier curve for RPA2 nuclear protein expression and BCSS in ER + cohort with endocrine therapy. F Kaplan–Meier curve for RPA2 nuclear protein expression and BCSS in triple negative (TN) in the whole cohort. G Kaplan–Meier curve for RPA2 mRNA expression and breast cancer-specific survival (BCSS) in the whole cohort. Survival rates were determined using Kaplan–Meier method and compared by the log-rank test. All analyses were conducted using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS, version 22, Chicago, IL, USA) software for windows. P value of less than 0.05 was identified as statistically significant.