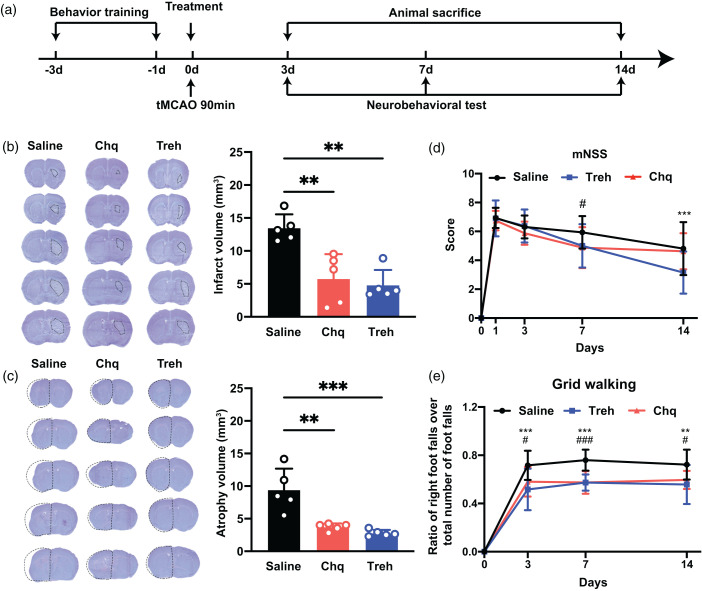
Figure 3.
The increase of PGRN reduced brain infarct volume and promoted neurobehavioral recovery after tMCAO. (a) Experimental scheme. (b) Representative cresyl violet-stained brain sections at 3 days of tMCAO mice treated with saline, chloroquine, or trehalose, n = 5 per group. The brain infarct area was circled by the dashed line, and bar graph showed the quantitative comparison of the infarct volume, **p < 0.01. Data are presented as mean ± SD. (c) Brain atrophy at 14 days were also detected by Cresyl violet in saline, chloroquine, and trehalose group, the dashed line represented brain atrophy. Bar graph showed the brain atrophy volume, n = 5 per group, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Data are presented as mean ± SD and (d–e) Neurobehavioral recovery was assessed by mNSS (d), and Grid walking tests (e), n = 9–15 per group, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (saline vs Treh), #p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001 (saline vs Chq), Data are presented as mean ± SD.