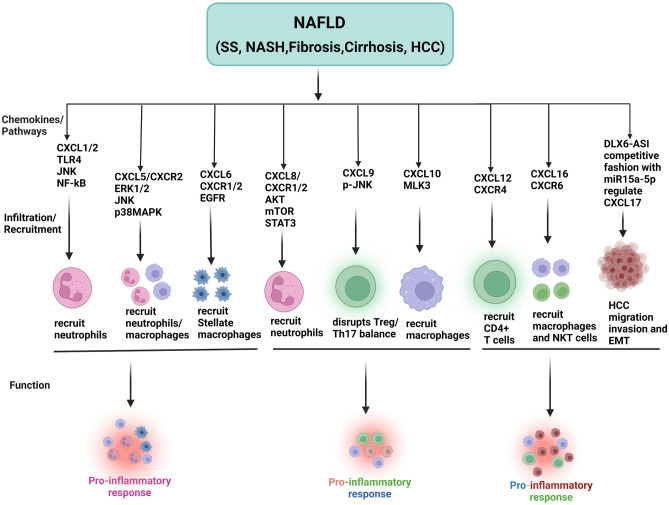
Fig. 5.
The role of CXC chemokines in the NAFLD. CXCL1 and CXCL2 recruit neutrophils via TLR- 4, JNK and NF-kB signaling, which induce inflammation. CXCL5 recruits neutrophiles through the ERK1/2/JNK and p38MAPK pathways, which plays an important role in the pro-inflammatory process. CXCL6 and receptor CXCR1 and CXCR2 recruits stellate macrophages by EGFR mechanism as a result pro-inflammatory response occur, CXCL8 and its receptors, CXCR1 and CXCR2, recruit neutrophils through the AKT/mTOR/STAT3 pathways, causing hepatocyte injury and inflammation. CXCL9 disrupts the Treg/Th17 via the p-JNK pathway, which acts as a pro-inflammatory signal. CXCL10 recruits the macrophage chemotaxis via MLK3 mechanism and produces a pro-inflammatory response. CXCL12 and its receptor CXCR4 recruit CD4+ T cells in the results of liver injury. CXCL6 and its receptor, CXCR6/CXCR6 axis, primarily recruit macrophages and NKT cells and produce proinflammatory response. DLX6-AS1 in HCC-derived exosomes modulates CXCL17 by binding to miR-15a-5p in a competitive fashion, which in turn promotes HCC migration, invasion, and EMT. Created with BioRender.com