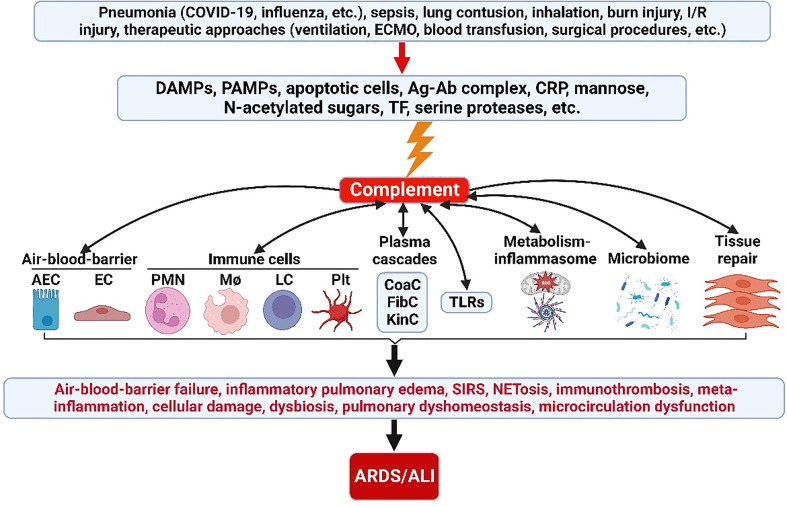
Figure 2.
ComC in the pathogenesis of ARDS/ALI. A variety of acute insults trigger complement activation via DAMPs, PAMPs, apoptotic cells, Ag-Ab complex, CRP, mannose, N-acetylated sugars, TF and serine proteases. The activated ComC resides upstream of immunity and acts as a vital nexus of the pathobiological connectome for ARDS/ALI. AEC, alveolar epithelial cell; Ag-Ab, antigen-antibody; ALI, acute lung injury; ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; CoaC, coagulation cascade; ComC, complement cascade; CRP, C-reactive protein; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; EC, endothelial cell; ECMO, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; FibC, fibrinolytic cascade; I/R, ischemia/reperfusion; KinC, kinin cascade; LC, lymphocyte; NETosis, neutrophil extracellular trap formation; PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; PICS, persistent inflammation/immunosuppression and catabolism syndrome; plt, platelet; PMN polymorphonuclear neutrophil; SIRS, systemic inflammatory response syndrome; TF, tissue factor; TLRs, toll-like receptors; MΦ, macrophage.