Abstract
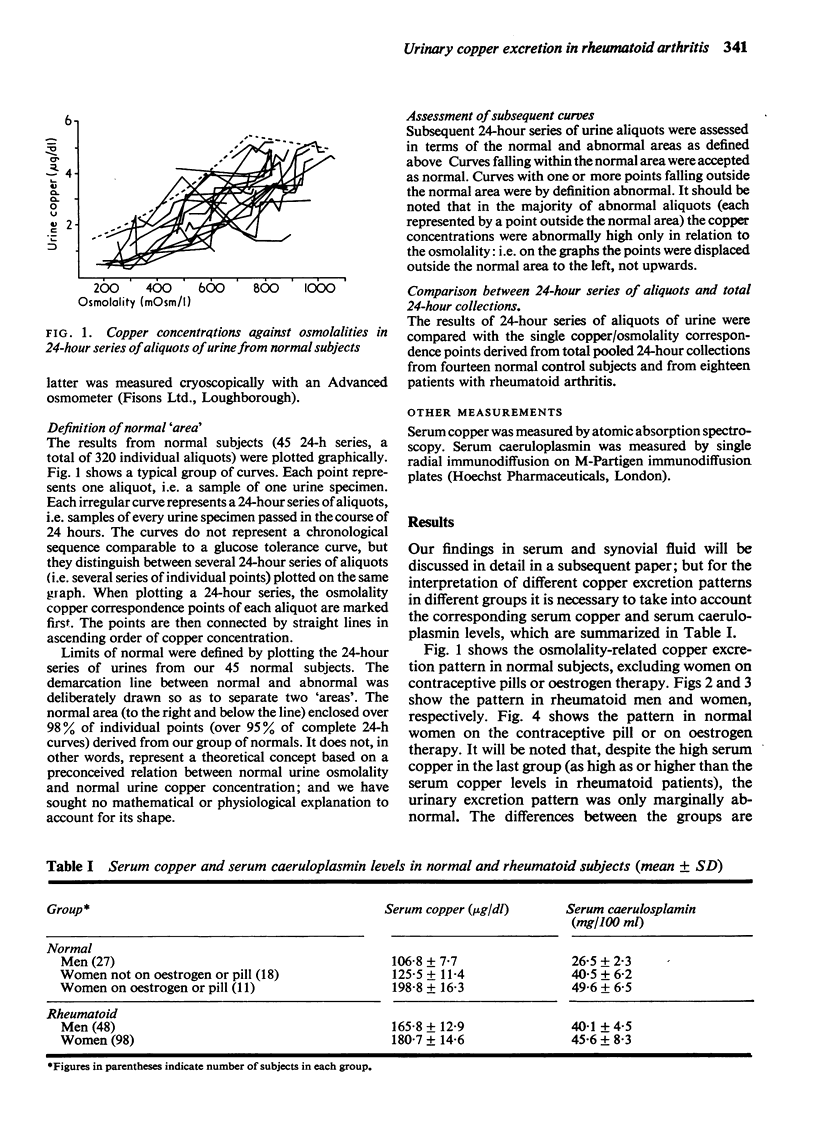
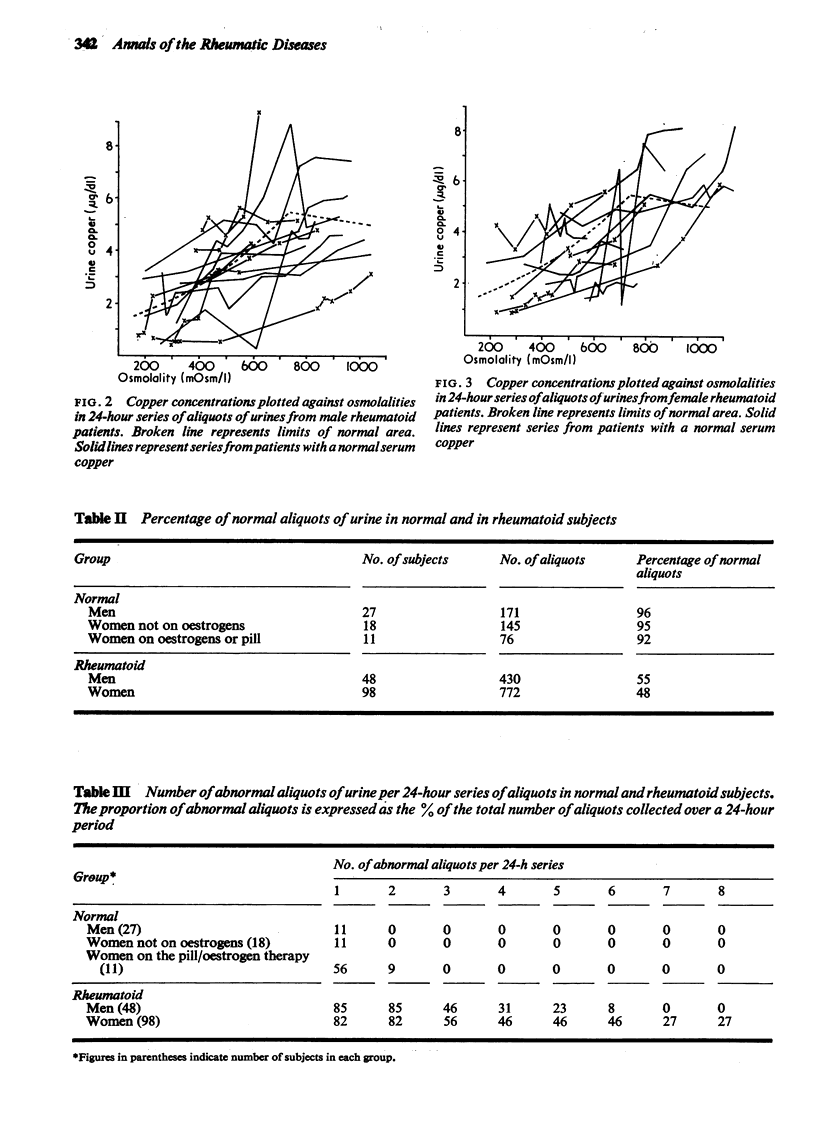
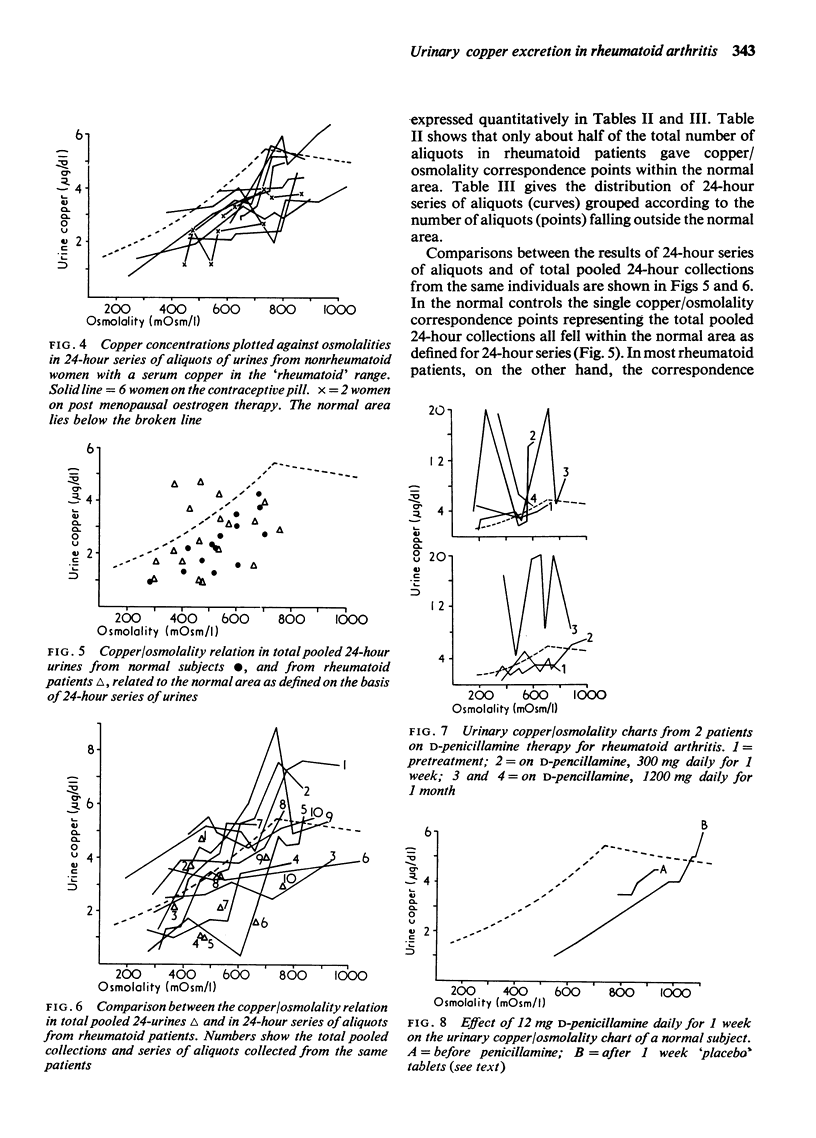
The pattern of urinary copper excretion in relation to urine osmolality (as shown by series of aliquots of urine) was studied in rheumatoid patients and in control groups. Rheumatoid patients showed an abnormal copper excretion pattern compared with nonrheumatoid subjects. This was not a direct function of the raised serum copper in rheumatoid disease. Measurements based on 24-hour series of aliquots of urine (as distinct from total pooled 24-hour collections) have been shown to be a useful and sensitive method for studying copper excretion patterns.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bulger R. J., Healey L. A., Polinsky P. Renal abnormalities in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1968 Jul;27(4):339–344. doi: 10.1136/ard.27.4.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burry H. C. Reduced glomerular function in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1972 Jan;31(1):65–68. doi: 10.1136/ard.31.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day A. T., Golding J. R., Lee P. N., Butterworth A. D. Penicillamine in rheumatoid disease: a long-term study. Br Med J. 1974 Feb 2;1(5900):180–183. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5900.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dormandy T. L. Osmometry. Lancet. 1967 Feb 4;1(7484):267–270. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91324-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGELIUS N. INDOMETHACIN: A NEW ANTI-RHEUMATIC DRUG. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1965;11:35–39. doi: 10.3109/rhe1.1965.11.issue-1-4.06. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber D. A. Increased copper ligand reactivity in the urine of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1966 Dec;9(6):795–803. doi: 10.1002/art.1780090607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halsted J. A., Hackley B. M., Smith J. C., Jr Plasma-zinc and copper in pregnancy and after oral contraceptives. Lancet. 1968 Aug 3;2(7562):278–279. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92375-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huskisson E. C., Wojtulewski J. A., Berry H., Scott J., Hart F. D., Balme H. W. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with fenoprofen: comparison with aspirin. Br Med J. 1974 Feb 2;1(5900):176–180. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5900.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe I. A. The treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and necrotizing vasculitis with penicillamine. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Jul-Aug;13(4):436–443. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskelo P., Kekki M., Virkkunen M., Lassus A., Somer T. Serum ceruloplasmin concentration in rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriasis and sarcoidosis. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1966;12(4):261–266. doi: 10.3109/rhe1.1966.12.issue-1-4.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorber A., Cutler L. S., Chang C. C. Serum copper levels in rheumatoid arthritis: relationship of elevated copper to protein alterations. Arthritis Rheum. 1968 Feb;11(1):65–71. doi: 10.1002/art.1780110109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLER W., KLUTHE R., MULLER H. [On the diagnosis of the activity of chronic rheumatic diseases, with special reference to the quantitative determination of haptoglobins and caeruloplasmin]. Z Rheumaforsch. 1963 Feb;22:1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedermeier W. Concentration and chemical state of copper in synovial fluid and blood serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1965 Nov;24(6):544–548. doi: 10.1136/ard.24.6.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


