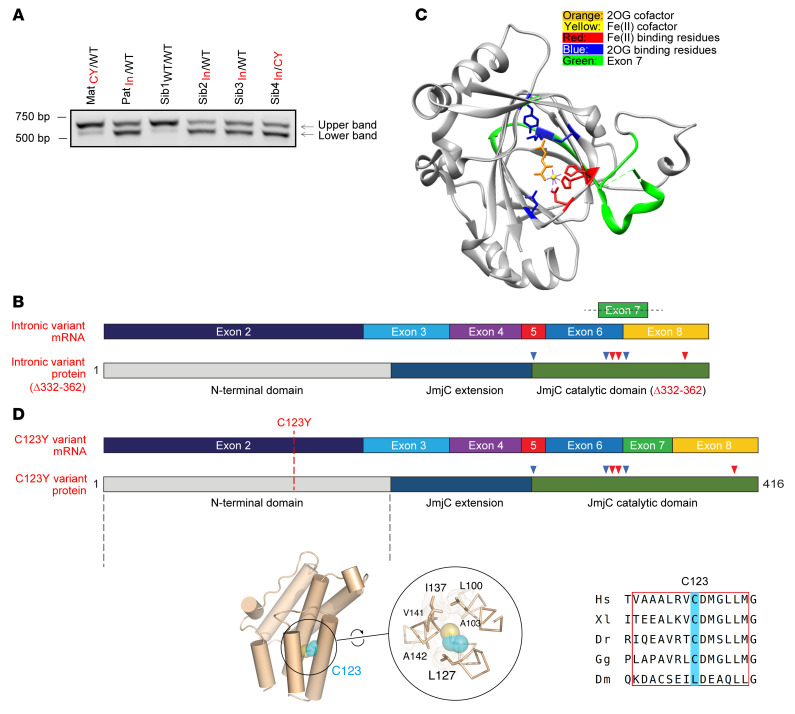
Figure 2. Patient variants affect JMJD5 mRNA splicing and enzyme structure.
(A) Carriers of the intronic variant express an altered JMJD5 mRNA (lower band). JMJD5 cDNA from exon 3 to the 3′-UTR was amplified from the indicated samples and separated by gel electrophoresis. The coding sequence of the wild-type (WT) JMJD5 mRNA (ENST00000286096.8, NM_024773) spanning this region is 706 bp (upper band). CY, C123Y; In, intronic mutant. (B) Graphical representation of the incorrectly spliced intronic variant mRNA (top) and protein (bottom) demonstrating the loss of sequence integral to the catalytic domain (compare with the correctly spliced mRNA in D). Fe(II)- and 2OG-binding residues are marked by red and blue arrowheads, respectively. (C) Structure of the catalytic domain of JMJD5 (Protein Data Bank: 4GAZ) with critical catalytic residues labeled. The region encoded by exon 7 that is missing from JMJD5Δ332–362 is highlighted in green. (D) Graphical representation of the C123Y JMJD5 mRNA and protein. The position of the C123Y missense variant within exon 2 and the JMJD5 N-terminus is highlighted (top). Structural predictions suggest that the JMJD5 N-terminus is predominantly α-helical (bottom left; also see Supplemental Figure 12). C123 is highly conserved (bottom right) and predicted to be located within a hydrophobic environment on one side of an amphipathic α-helix within a TPR domain (bottom middle; also see Supplemental Figure 12).