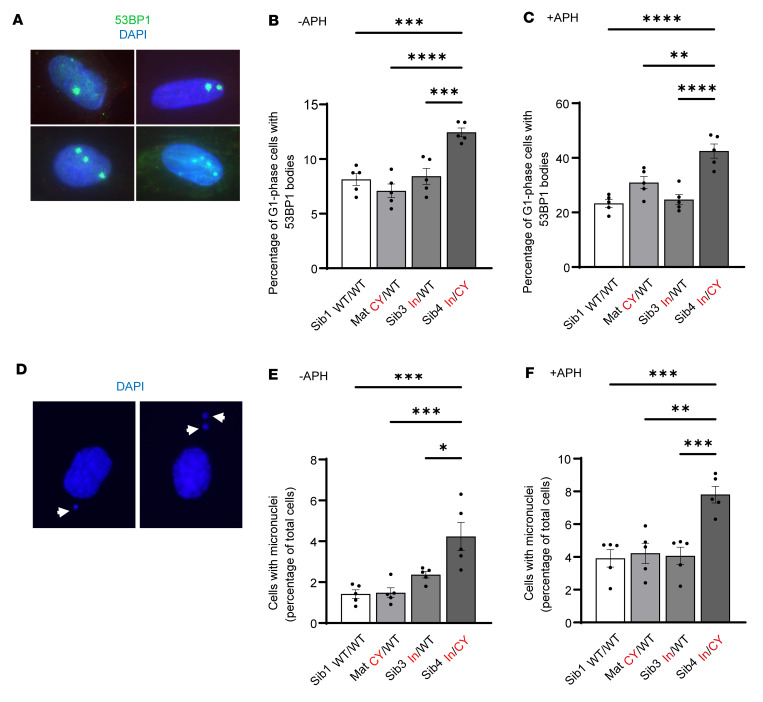
Figure 4. Biallelic JMJD5 pathogenic variants are associated with increased markers of replication stress.
Immortalized fibroblasts were monitored for 2 commonly used markers of replication stress (micronuclei and 53BP1 bodies). The affected Sib4In/CY fibroblasts show significantly increased replication stress. (A) 53BP1 bodies were counted using immunofluorescence staining and distinguished from 53BP1 foci based on their size and presence only in G1 cells (using costaining for CENPF). Shown are examples of cells with different numbers of 53BP1 bodies. (B) 53BP1 bodies in untreated cells were significantly increased in Sib4In/CY immortalized fibroblasts. APH indicates aphidicolin, a DNA polymerase inhibitor that is an established replication stress stimulus (see below). (C) 53BP1 bodies were also significantly increased in Sib4In/CY immortalized fibroblasts treated with APH (0.5 μM for 48 hours). (D) Micronuclei were counted following DAPI staining. Shown are 2 examples of cells with micronuclei. (E) Micronuclei were significantly increased in untreated Sib4In/CY immortalized fibroblasts. (F) Micronuclei were also significantly increased in Sib4In/CY immortalized fibroblasts treated with APH. (B, C, E, and F) Data represent mean ± SEM from 5 independent experiments. For 53BP1 bodies, a minimum of 300 cells were counted per sample. For micronuclei, a minimum of 500 cells were counted per sample. Statistical analyses used 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test; *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001.