Fig. 1 |. Development of ssCTS templates for high yield knock-in.
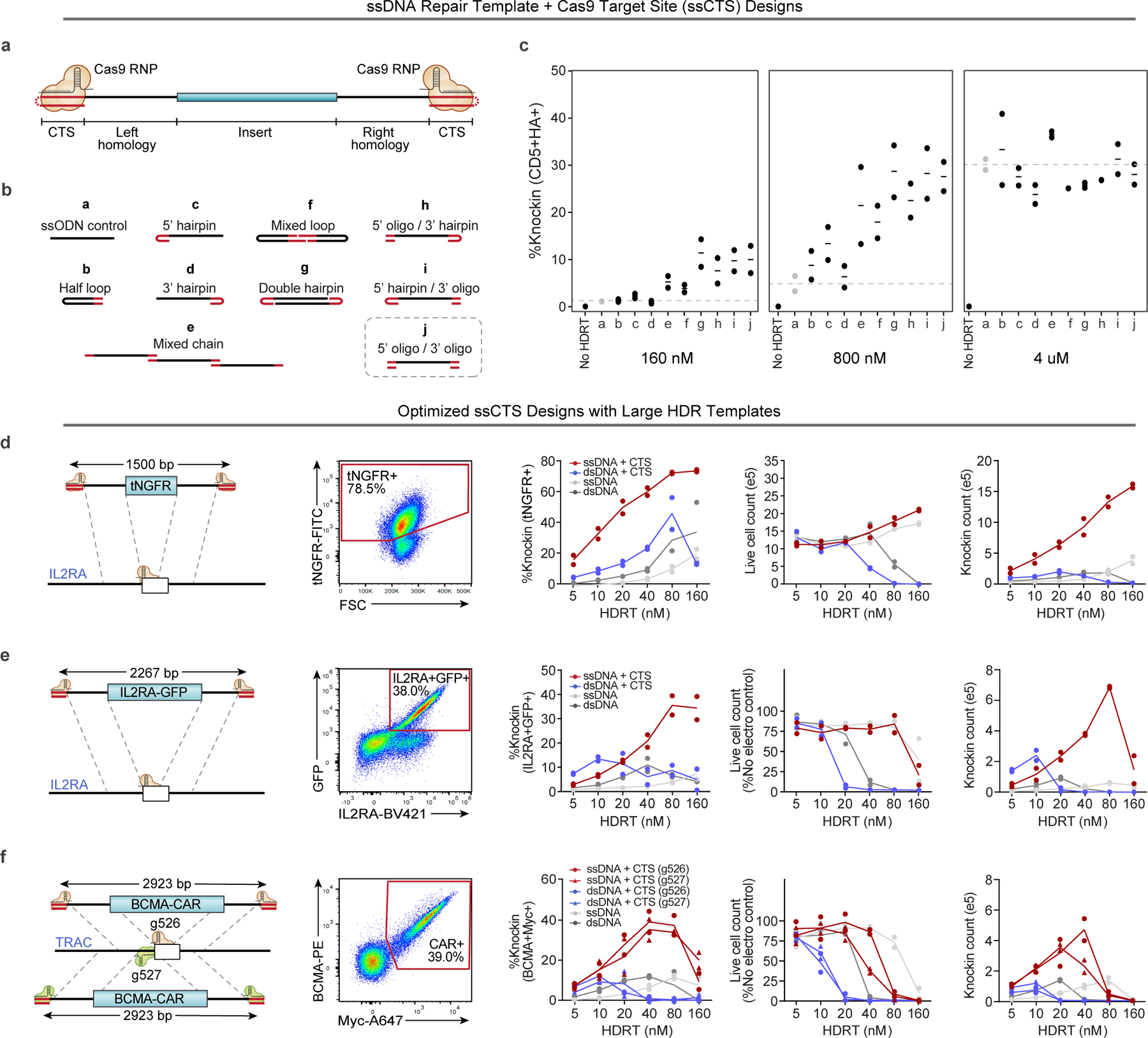
a, Diagram of hybrid ssDNA HDRT designs incorporating CTS sites. b, Panel of ssCTS designs tested. c, Knock-in efficiency for each ssCTS design using a CD5-HA knock-in construct at 160 nM–4 μM concentration assessed by flow cytometry. Dotted line represents mean knock-in percentage for control ssDNA HDRTs without CTS (construct a, gray). d–f, Knock-in strategy, gating, knock-in efficiency, live cell counts and knock-in cell counts are shown for large ssCTS templates including a tNGFR knock-in at the IL2RA locus (d), a IL2RA-GFP fusion protein knock-in to the IL2RA locus (e) or two different HDRTs inserting a BCMA-CAR construct at TRAC locus via two different gRNAs (g526 and g527) (f). Each experiment was performed with T cells from two independent healthy human blood donors represented by individual dots plus mean. CTS, Cas9 target site; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; ssCTS, ssDNA HDRT + CTS sites. This figure was generated in part using graphics created by Biorender.com.
