Extended Data Fig. 3 |. Evaluation of ssCTS design and mechanism with large HDRTs.
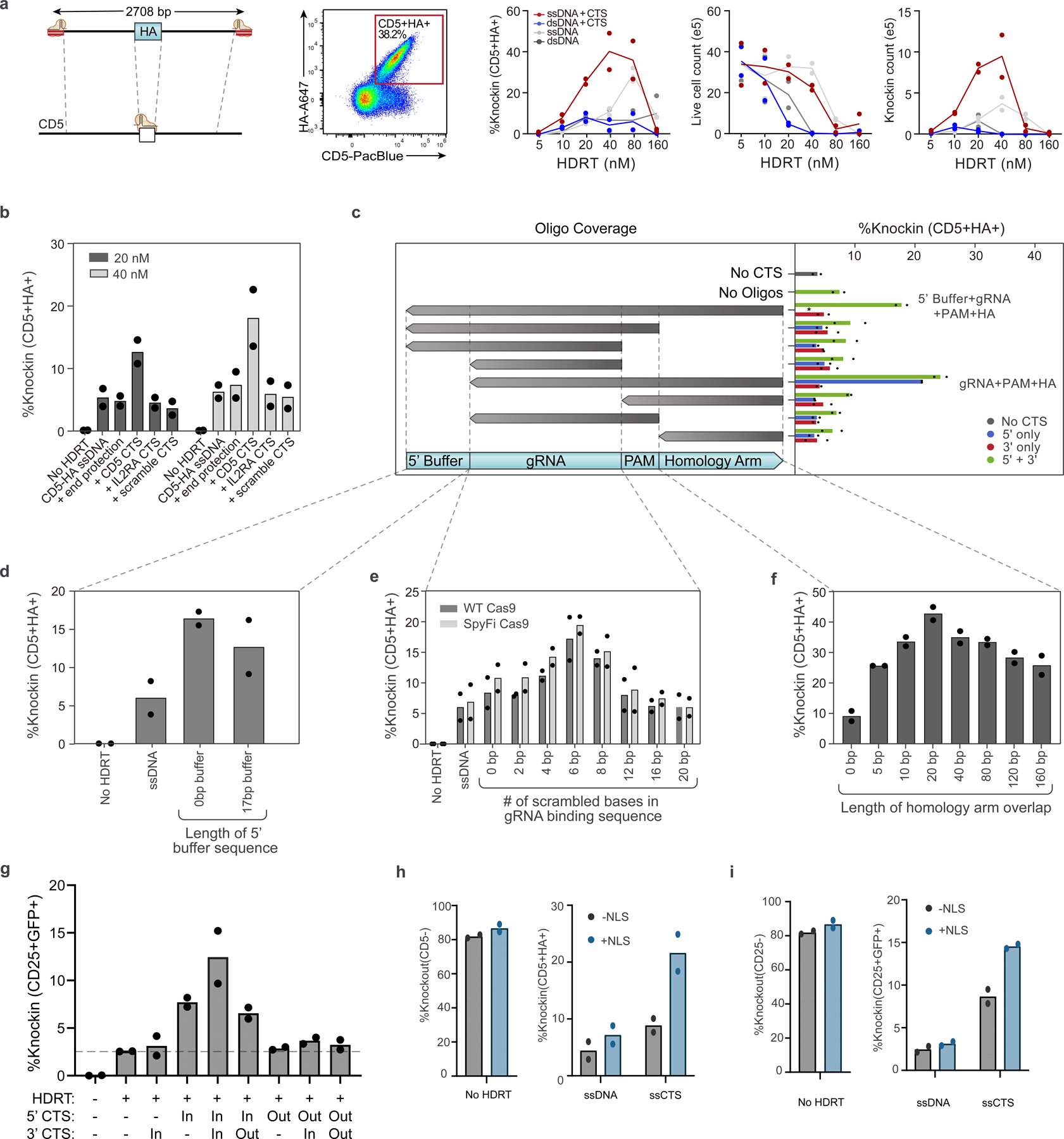
(a-f) Comparison of different CTS designs with a large ~2.7 kb CD5-HA knock-in construct. (a) Diagram of long CD5-HA knock-in strategy, representative flow cytometry plot, percent knock-in, live cell counts, and knock-in cell yield counts. (b) Comparison of CTS with a gRNA target sequence that is specific for the cognate RNP ( + CD5 CTS), an alternative gRNA sequence (+ IL2RA CTS), a CTS incorporating a PAM site and scrambled gRNA sequence (+ scramble CTS), or an equivalent amount of dsDNA within the 5’ end of the homology arm (+ end protection). (c) Comparison of complementary oligos covering different regions of the CTS and surrounding sequences. Constructs with CTS sites on both 5’ and 3’ end (green bars), 5’ end only (blue bars), or 3’ end only (red bars) are shown on the right panel. (d) Evaluation of varied 5’ ends including different length of buffer sequence upstream of the CTS site. *indicates no data available for the marked column. (e) Comparison of CTS with different numbers of scrambled bases at the 5’ end of the gRNA target sequence using WT or SpyFi Cas9. (f) Length of homology arm that is covered by the complementary oligonucleotide. (g) Evaluation with and without (‘−’) CTS sites on the 5’ and 3’ end of long ssDNA IL2RA-GFP HDRTs with PAM facing inwards toward the homology arm (‘In’) or outwards away from the homology arm (‘Out’). (h-i) Comparison of knockout and knockin with large CD5-HA (h) or IL2RA-GFP (i) ssDNA and ssCTS HDRTs using RNPs formulated with Cas9 +/− NLS sequences. Each experiment was performed with T cells from 2 independent healthy human blood donors represented by individual dots + mean. RNP = Ribonucleoprotein, CTS = Cas9 Target Site, ssCTS = ssDNA HDRT + CTS sites, PAM = Protospacer Adjacent Motif, HDRT = homology-directed-repair template.
