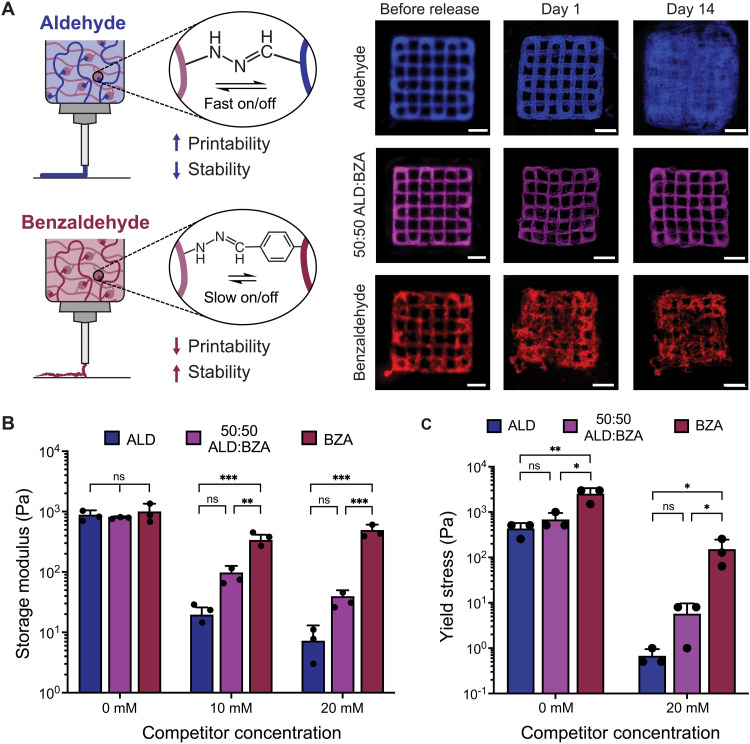
Fig. 3. HELP ink materials can be optimized to improve printability and long-term stability.
(A) Schematic depicting that the HA component of HELP can be modified with either an ALD group (faster bond exchange rate) or a BZA group (slower bond exchange rate). Representative images of printed lattices show that changing the ratio of ALD:BZA affects ink printability and the stability of printed structures over time. Scale bars, 2 mm. (B) Tuning the ratio of ALD:BZA does not affect the storage modulus of HELP hydrogels. The addition of competitor has a smaller effect on the storage modulus of BZA-only HELP hydrogels as compared to that of ALD-only hydrogels and ALD:BZA blends (n = 3, means ± SD, ordinary one-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparisons correction, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). (C) Yield stress behavior changes as a function of cross-linking kinetics (i.e., ALD-only, 50:50 ALD:BZA, and BZA-only) and with the addition of the competitor (n = 3, means ± SD, ordinary one-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparisons correction, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). ns, not significant.