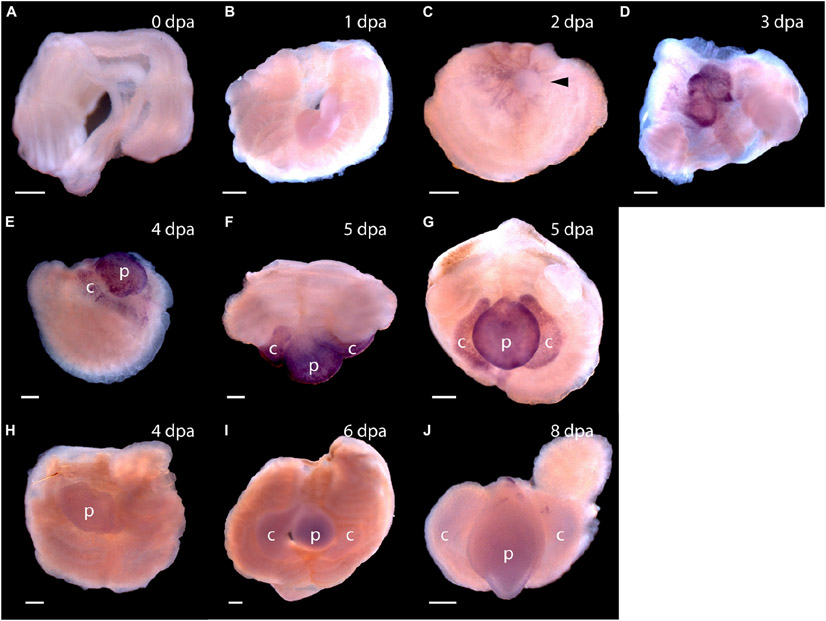
FIGURE 5 ∣.
Expression of stem cell genes Pf-SoxB1 and Pf-Klf1/2/4 during head regeneration. (A–G) Whole mount in situ hybridization of Pf-SoxB1. At 0 days post-amputation (dpa) (A) and at 1 dpa (B), no signal is detected. (C) At 2 dpa, a fine, reticulated signal appears at the swollen edges of the cut body wall being pulled into the closing wound. The arrowhead marks an unlabeled, rounded bleb of swollen body wall not yet pulled into the wound. (D) At 3 dpa, a strong signal appears only in the blastema. This blastema appears as two parts. These parts usually merge into one as they grow. (E) At 4 dpa, signal appears only in blastema with signal showing in the nascent collar as well as in the proboscis. (F) At 5 dpa, dorsal view, signal appears only in the blastema with no signal along the dorsal midline where Pf-Pou3 and Pf-Msxlx signals are prominent (see Figures 4A-G for Pf-Pou3 and Figures 4F-H for Pf-Msxlx). (G) At 5 dpa, there is signal throughout the blastema, but no signal in the dorsal trunk. Dorsal is up in all frames except (F) where the dorsal surface is facing the viewer. (H–J) In situ hybridization of Pf-Klf1/2/4. (H) At 4 dpa, (I) at 6 dpa, and (J) at 8 dpa, definite, but weak signal spread generally throughout the blastema and regenerating tissue. p, nascent proboscis; c, nascent collar. Scale bars = 0.25 mm.