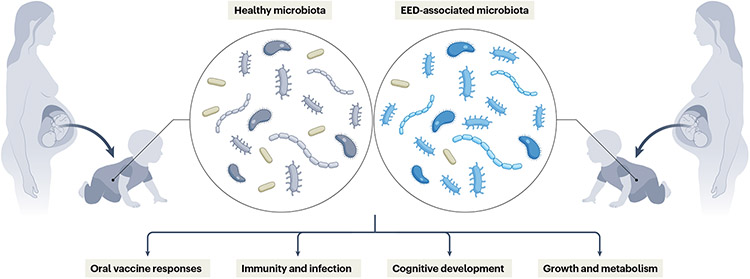
Fig. 4 ∣. Long-term implications of maternal environmental enteric dysfunction.
Maternal gut inflammation is a risk factor for poor fetal growth and adverse birth outcomes in multiple enteropathies. Infants inherit a substantial proportion of their gut microbiota from their mothers; thus, the maternal microbiome can play a part in shaping immunity in both mother and child. Altered maternal and infant gut function can have lifelong health consequences, including susceptibility to infection, oral vaccine responses, cognitive development and metabolic tone. EED, environmental enteric dysfunction.