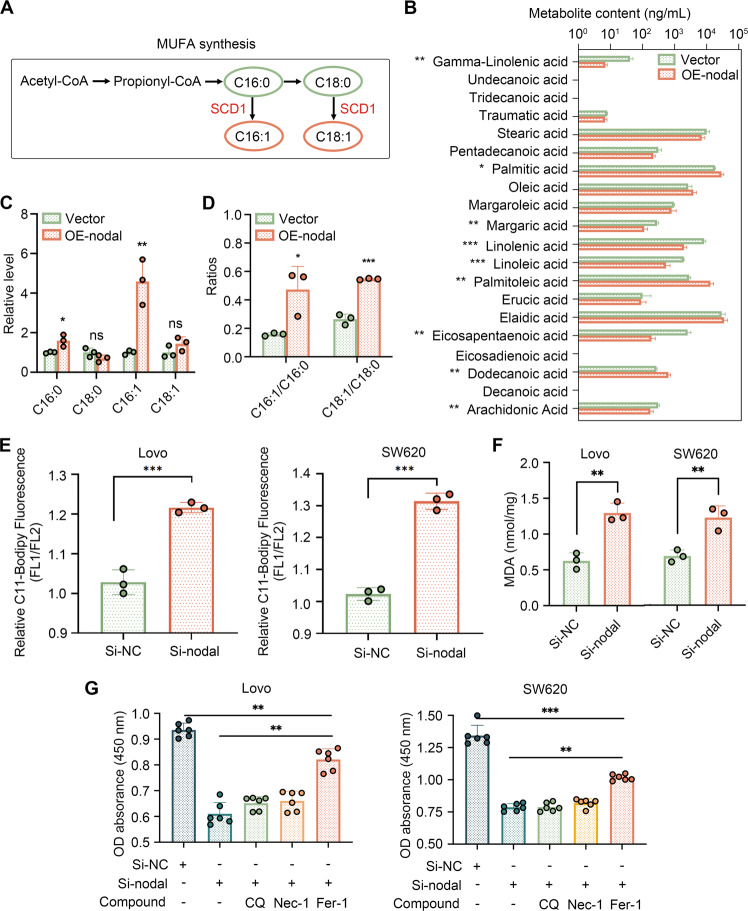
Fig. 4. Nodal regulates fatty acid desaturation and lipid peroxidation.
A Schematic diagram of the synthesis of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs). Monosaturated fatty acids: stearic acid (C18:0) and palmitic acid (C16:0); MUFAs: oleic acid (C18:1) and palmitoleic acid (C16:1). B The content of various fatty acids in the vector and oe-Nodal groups. C The relative level of the four main fatty acids in oe-Nodal group compared with the vector group. D Fatty acid desaturation levels were evaluated based on the ratio of MUFAs to the corresponding monosaturated fatty acids. E Flow cytometry was performed to analyse lipid peroxidation in Lovo and SW620 cells stained with BODIPY™ C11 after Nodal knockdown. Fluorescence channel (FL)1 channel (excitation, 488 nm) was used to measure the oxidised lipid, whereas FL2 channel (excitation, 561 nm) was used to measure the unoxidised lipid. The proportion of lipid peroxidation cells was quantified according to the fluorescence intensity ratio of FL1 to FL2. F Malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were detected in Lovo and SW620 cells after Nodal knockdown. G Cell viability was measured via CCK8 assay after cells in the si-Nodal group were treated with several cell death inhibitors for 48 h. Cell death inhibitors: ferrostatin-1 (Fer-1, a ferroptosis inhibitor, 1 μM), chloroquine (CQ, an autophagy inhibitor, 10 μM), and necrostatin-1 (Nec-1, a necroptosis inhibitor, 10 μM). (∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗∗∗P < 0.001).