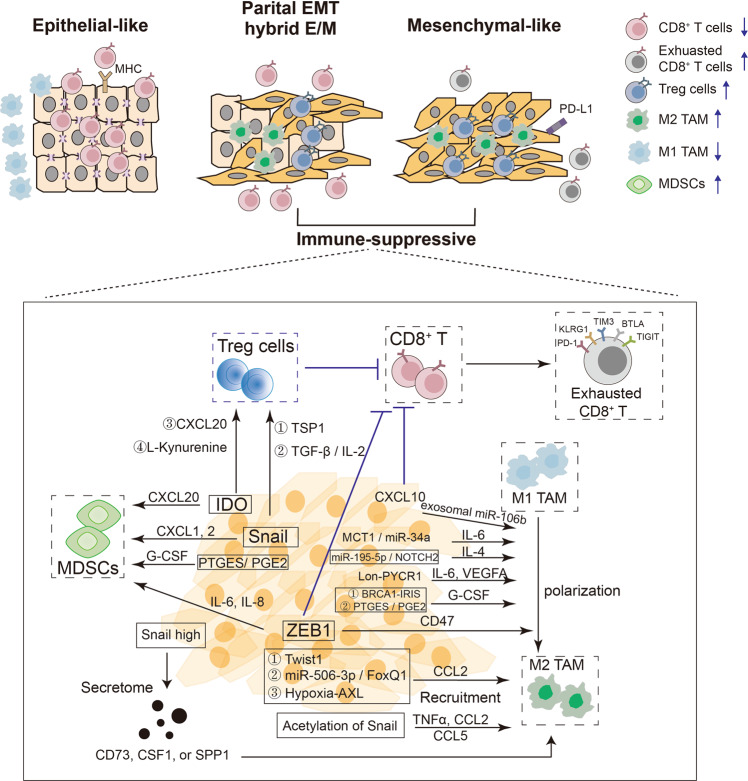
Fig. 4.
EMP impacts cancer cell-immune cell interactions, shaping the immunosuppressive TME. Cancer cell clusters that exhibit more epithelial-like, more mesenchymal-like or mixed epithelial-like and mesenchymal-like phenotypes interact differently with different types of immune cells in the TME. Compared with epithelial-like tumors, tumors with a partial EMP or mesenchymal-like phenotypes generate an immunosuppressive TME, in which EMP-TFs or their upstream activators mediate the secretion of specific cytokines or chemokines to recruit immunosuppressive cells (Tregs, TAMs, and MDSCs) and thereby exclude CD8+ CTLs to the periphery or dampen CD8+ T cells with exhausted CD8+ T cell features, such as increased expression of PD-1, KLRG1, TIM3, BTLA or TIGHT. AXL receptor tyrosione kinase of the TAM family, BRCA1-IRIS in-frame reading of intron 11 splice variant, BTLA B and T lymphocyte attenuator, CD8 cluster of differentiation 8, E/M epithelial/mesenchymal, EMT epithelial to mesenchymal transition, EMP epithelial mesenchymal plasticity, CCL chemokine (C-C motif) ligand, CXCL chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand, IDO indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, IL interleukin, G-CSF granulocyte-colony stimulating factor, KLRG1 killer cell lectin like receptor G1, MDSCs myeloid-derived suppressor cells, PD-1 programmed cell death protein 1, PTGES/PGE2 prostaglandin E synthase/prostaglandin E2, Snail Snail family transcriptional repressor 1, SPP1 ostepontin, TAMs tumor associated macrophages, TIGIT T-cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain, TIM3 T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing-3, TGF-β transforming growth factor β, TF transcription factor, TNF tumor necrosis factor, TME tumor microenvironment, Treg regulatory T cell, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor, ZEB1 zinc finger E-Box binding homeobox factor 1