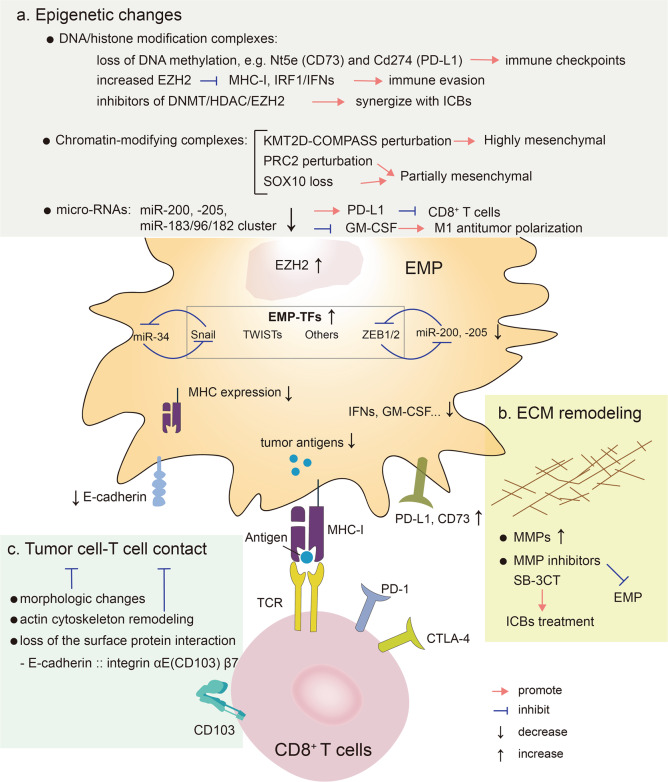
Fig. 5.
Other EMP-associated changes and immune resistance. Beyond the “classical” activation of EMT transcription factors and effectors, EMP is connected with additional pleiotropic changes, such as epigenetic alterations (a), ECM remodeling (b) and tumor cell-T cell contact (c). The connection between these EMP-associated changes and immune resistance is shown. Epigenetic alterations include DNA/histone modification, chromatin-modifying and microRNAs changes. DNA methylation was lost in some well-known regulators of immune evasion, including Nt5e (CD73) and Cd274 (PD-L1). Increased EZH2 levels can suppress the expression of MHC-I and mitigate IFR1 mediated IFNs signaling. Epigenetic agents, including HDAC inhibitors, DNA methyltransferase inhibitors, and EZH2 inhibitors, display promising synergies with ICBs in patients via activating immunomodulatory mechanisms, such as enhancing HLA class I antigen processing machinery (APM) component expression and function. The changes of chromatin-modifying complexes, such as KMT2D-COMPASS or PCR2 perturbation and loss of SOX10, can affect the cancer cell EMP states. Some microRNAs, including miR-200/miR-200c and microRNA-183/96/182 cluster, are repressed in cancer cells displaying EMP, which may inhibit the immune response. ECM remodeling, including increased MMPs, can stimulate EMP progression. SB-3CT, an MMP2/9 inhibitor, could improve the efficacy of anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA-4 treatment. Morphologic changes, actin cytoskeleton remodeling and loss of the surface protein interaction can affect the cancer cell-T cell contact, resulting in different CTL-mediated killing effects. CD8 cluster of differentiation 8, COMPASS a complex of proteins associated with a trithorax-related SET domain protein, CTLA-4 cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4, EMP epithelial mesenchymal plasticity, EMP-TFs EMP inducing transcription factors, DNMT DNA methyltransferase, E-Cadherin epithelial cadherin, ECM extracellular matrix, EZH2 enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit, GM-CSF granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, HDAC histone deacetylase, KMT2D-COMPASS Histone methyltransferase complex, Nt5e ecto-5′-nucleotidase, miR micro RNA, MHC-I major histocompatibility complex I, MMPs proteases of the matrix metalloproteinases, ICB immune check point blockade, IFNs interferons, IRF1 interferon regulatory factor 1, SB-3CT a selective MMP2/9 inhibitor, Snail snail family transcriptional repressor 1, SOX10 sex-determining region Y-box 10, PD-1 programmed cell death protein 1, PD-L1 programmed death-1 ligand 1, PRC2 polycomb complex 2, TCR T cell receptor, TF transcription factor, TWISTs the basic helix–loop–helix factors, ZEB1/2 zinc finger E-Box binding homeobox factor 1/2