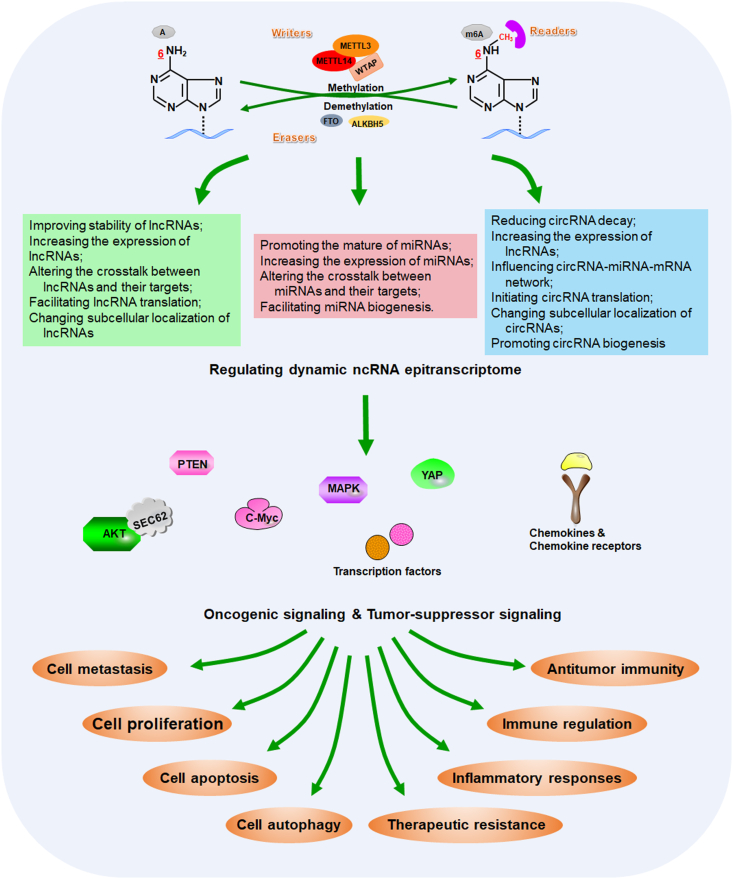
Figure 2.
Multiple functions of m6A modifications on ncRNAs in the control of cancer pathogenesis and treatment. As the most prevalently and abundantly modified form, m6A RNA modification have been proven to function as a promising regulatory layer that coordinate multiple steps of ncRNA homeostasis, such as ncRNA stability, ncRNA–target interaction and subcellular localization. Aberrant m6A–ncRNA machinery could result in dysregulation of cancer-associated signaling pathways, which is involved in a variety of biological behaviors in cancers, especially like cancer development, immune regulation and therapeutic response.