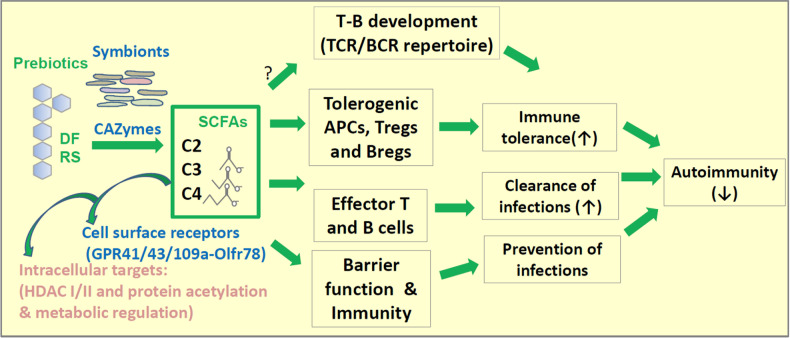
Fig. 1.
Regulation of immune tolerance by SCFAs. Dietary fiber (DF) and resistant starch (RS) are prebiotics that are processed by microbes to produce SCFAs. Intestinal SCFAs are best produced by certain symbionts expressing CAZymes and/or active SCFA production pathways. By triggering GPR signaling via GPR43, GPR41, GPR109A, and Olfr78, SCFAs affect distinct groups of cells in the body. Intracellular SCFAs, particularly propionate (C3) and butyrate (C4), function as natural HDAC inhibitors. It is expected that certain cell types with high expression of SCFA-transporting solute transporters can effectively concentrate SCFAs within cells for HDAC inhibition. HDAC inhibition triggers elevated gene expression and cell activation to boost tissue barrier functions and the activity of T and B cells. Optimal barrier functions and immune functions are important for preventing infections. HDAC inhibition by SCFAs also generates Tregs, Bregs, tolerogenic antigen presenting cells (APCs such as DCs), and IL-10-producing macrophages, all of which function to suppress inflammatory responses. Microbiota and SCFAs have the potential to shape the antigen receptor repertoire in developing lymphocytes to prevent autoimmunity