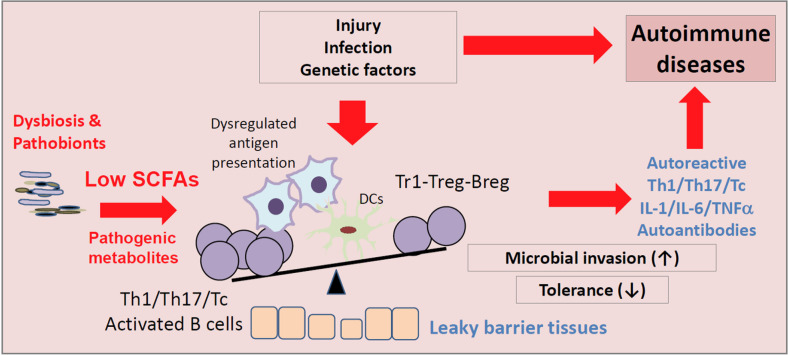
Fig. 2.
Regulation of immune cells important for immune tolerance by SCFAs. In diseased states following infection or injury, microbial dysbiosis and prolonged inflammatory responses work together to break immune tolerance. Microbial dysbiosis can lead to altered production of microbial metabolites, including decreased SCFAs. SCFA production deficiency may change the activities of APCs, T cells and B cells to generate autoreactive effector lymphocytes. In microbial dysbiosis, pathogenic metabolites, such as certain bile acid derivatives, formate, trimethylamine N-oxide, polyamines, and hydrogen sulfide, are produced instead of SCFAs. These metabolites damage tissues and increase the inflammatory activities of immune cells