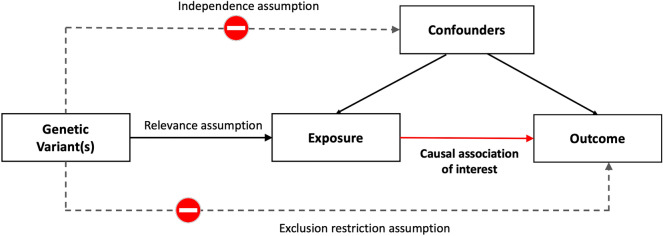
Figure 1.
Conceptual illustration of the Mendelian Randomization (MR) method. The causal association of interest is between the exposure (e.g., physical activity) and the outcome (e.g., cognitive function). Relevance assumption states that the genetic instruments are strongly associated with the exposure but are not associated with the confounders. The exclusion restriction assumption states that the genetic instruments are only indirectly associated with the outcome via the exposure. Thus, the solid paths are expected to exist, while the dashed paths are expected to be nonsignificant according to the core MR assumptions.