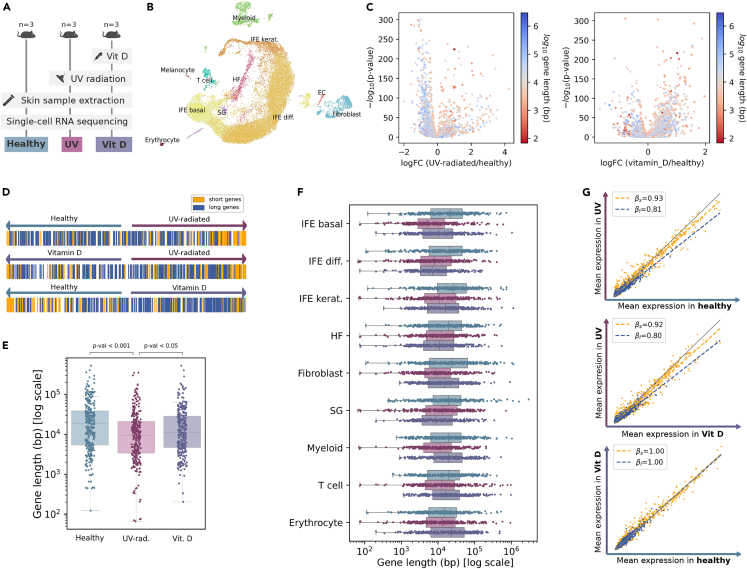
Figure 4.
Genotoxic UV exposure of young mouse skin mimics age-associated decrease in the expression of long genes
(A) Experimental workflow: mice were sorted into three groups (n = 3 per condition). The Vit D group was injected with a vitamin D treatment. All mice were shaved and irradiated, either with UV light (Vit D and UV groups) or with visible light (healthy). Skin samples were extracted and analyzed using scRNAseq.
(B) UMAP plot showing 11 cell types in the murine skin dataset (Lin et al., 2022). The samples corresponding to the three conditions were merged into a single dataset. Diff, differentiated. EC, endothelial cell. HF, hair follicle. IFE, interfollicular epidermis. Kerat, keratinocytes. SG, sebaceous gland.
(C) Volcano plots showing UV radiation-related gene overexpression without prior vitamin D treatment (left) and with the vitamin D treatment (right): -log10(p value) against the log2(fold change). DEGs were computed using the Wilcoxon method. Each gene is colored according to its log10-transformed gene length.
(D) Position of the top 200 shortest (yellow) and top 200 longest (blue) genes in the differential expression ranking. Genes are shown ranked according to their difference in mean expression between every pair of conditions and colored according to their length.
(E) Boxplots showing the log10(length) of the DEGs between conditions. Top 300 DEGs were computed between the three conditions (those differentially expressed in each of the conditions against the remaining two). The differences were statistically significant (p values correspond to the Tukey post-hoc test after ANOVA).
(F) Boxplots showing the log10(length) of the DEGs between conditions per cell type. The DEGs were computed between the three conditions for each cell type separately. Whiskers extend to the furthest datapoint within the 1.5∗IR.
(G) Scatterplots showing the mean expression in every pair of conditions: UV-radiated vs healthy skin (top), UV-radiated vs vitamin D treated skin (middle), and vitamin D-treated vs healthy skin (bottom). βs and βl correspond to the slopes of the multiple linear regression models with interaction fitted on the first and fourth quartiles (top 25% shortest and top 25% shortest genes), respectively.
See also Table S5.