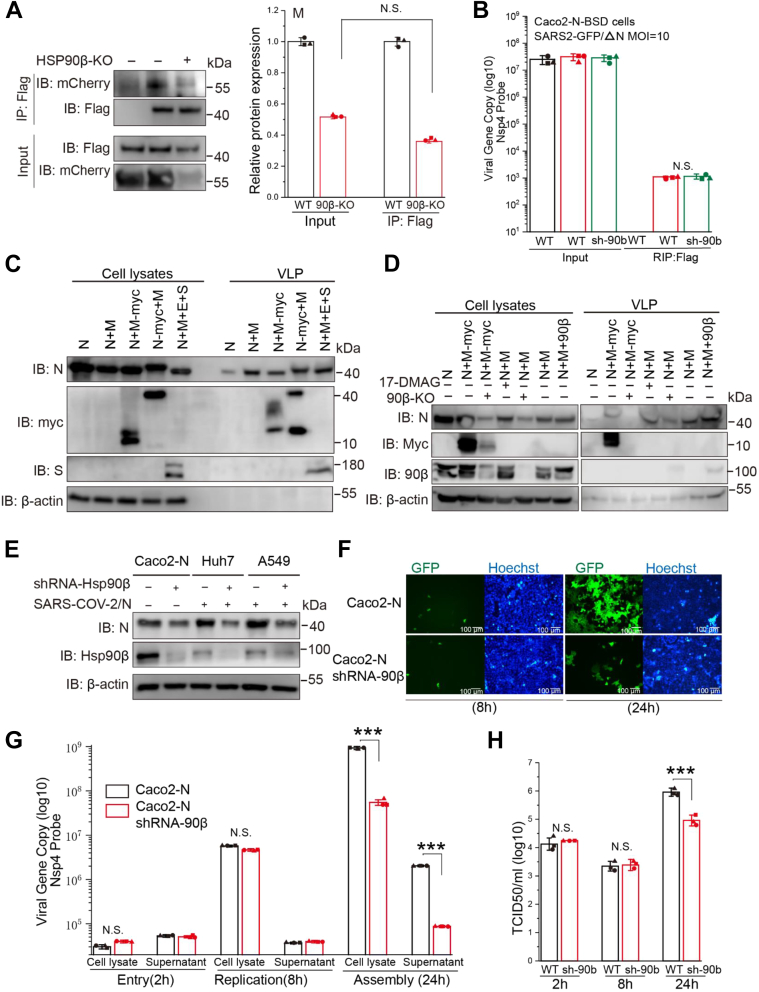
Figure 5.
Disruption of Hsp90 function diminishes efficient virion assembly of SARS-CoV-2.A, WT or 90β-KO HEK293T cells were transfected with M and N vectors and total cellular proteins were extracted. CoIP assay was performed using an anti-flag antibody. B, Caco-2-N-flag cells or Caco-2-N-flag shRNA-Hsp90β cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 GFP/ΔN virus at MOI = 1 for 8 h, and total cellular proteins were extracted. RNA immunoprecipitation was performed using an anti-flag antibody. C, SARS-CoV-2 VLP assembly and release. HEK293T cells were transfected with M, N, M-tagged myc (M-myc), N-tagged myc (N-myc) expression vectors individually or in various combinations. At 48 h post-transfection, supernatants and cells were collected and prepared for protein analysis as described in the Experimental procedures. D, WT and 90β-KO HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids for 36 h. Lysates and corresponding purified VLPs were analyzed by Western blot. E, Hsp90β knockdown decreases SARS-CoV-2 protein levels in various cell lines (Caco-2-N, Huh7, and A549). F–H, Caco-2-N cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 GFP/ΔN virus at MOI = 1. Viral load was detected in cell lysates or supernatant by one-step qRT-PCR at the indicated h postinfection. Viral titration was detected in supernatant by TCID50 assay; ∗p ≤ 0.05; ∗∗p ≤ 0.01; n.s.: Not significant. CoIP, coimmunoprecipitation; Hsp90, heat shock protein 90; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; TCID50, tissue culture ID50; VLP, virus-like particle.