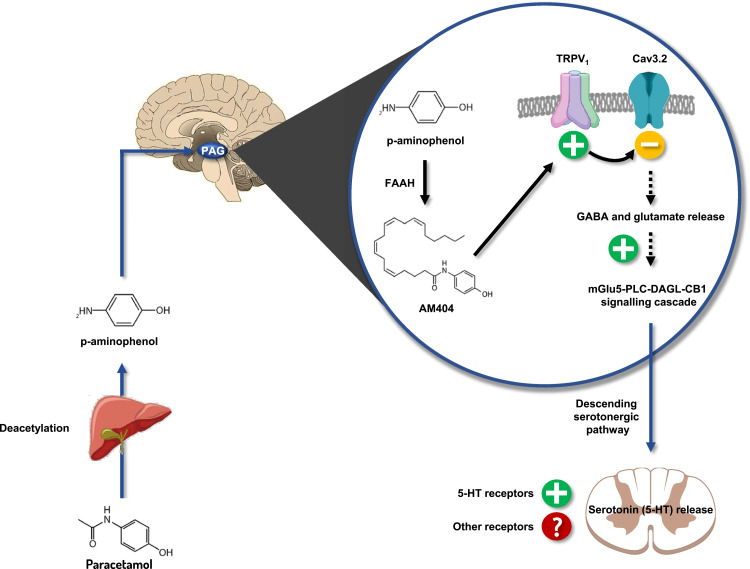
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the central mechanism of action of paracetamol to its antinociceptive activity. Paracetamol is deacetylated in p-aminophenol in the liver, then metabolized in the brain by FAAH into AM404. AM404 activates the TRPV1 channel‐mGlu5 receptor‐PLC‐DAGL‐CB1 pathway and co-activates the Cav 3.2 T-type calcium channel, which in turn reinforces the activity of the descending serotonergic pathways.