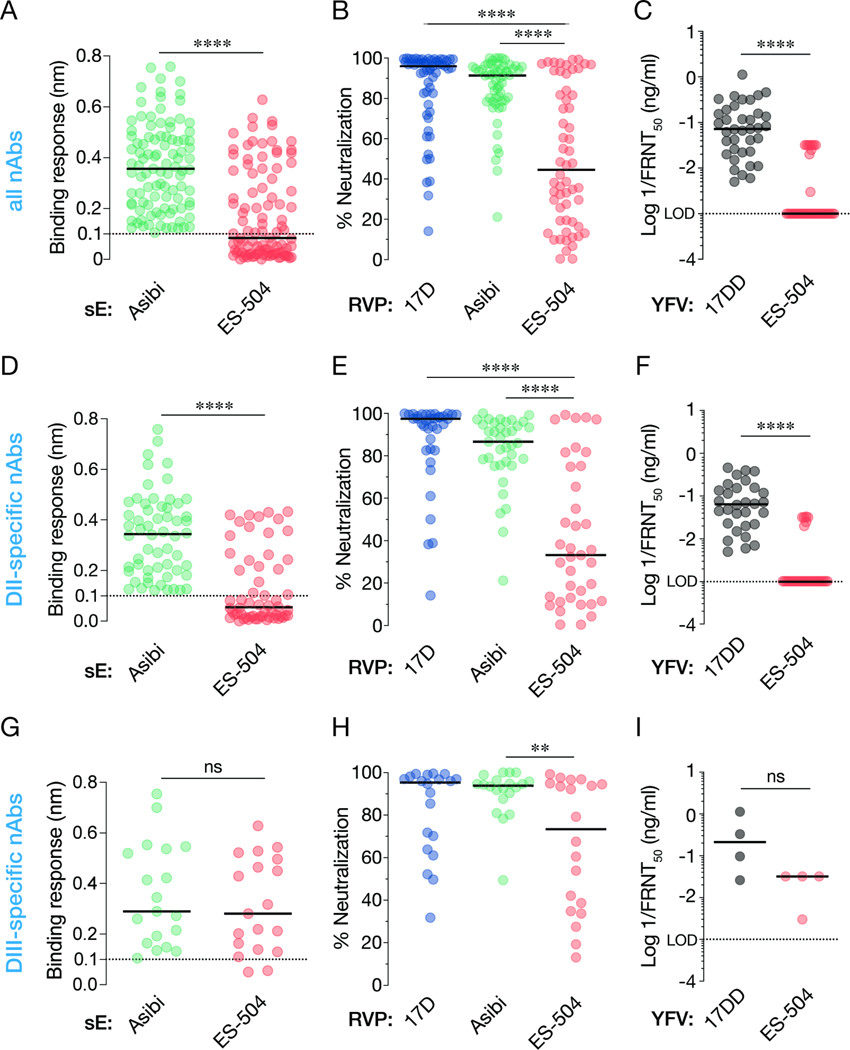
Figure 2. Binding and neutralization breadth of a panel of nAbs isolated from YF-17D vaccinees.
(A) 99 nAbs were tested for their binding response to recombinant, soluble E (sE) proteins from the indicated viruses by biolayer interferometry. (B) Neutralizing activities of selected nAbs (10 nM) against the indicated RVPs. Means, n=6–9 from three independent experiments, (C) Neutralizing activities of selected mAbs against the indicated authentic viruses. (D) A subset of nAbs comprising DII binders were evaluated for sE binding as in panel A. (E–F) Neutralizing activities of DII-specific nAbs against the indicated RVPs (E) and authentic viruses (F), as in panels B–C. (G–I) Binding (G) and neutralization activities (H–I) of DIII-specific nAbs, as in panels B–C. In all panels, lines indicate group medians. Groups in A, C, D, F, G, and I were compared by the Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test. Groups in B, E, H were compared by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s correction for multiple comparisons. **, P<0.002. ****, P<0.0001. ns, not significant. Only the significant comparisons are shown in panels B, E, H. LOD, limit of detection.